mindspore.ops.scatter_nd
- mindspore.ops.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape)[source]
Scatters a tensor into a new tensor depending on the specified indices.
Creates an empty tensor with the given shape, and set values by scattering the update tensor depending on indices. The empty tensor has rank \(P\) and indices has rank \(Q\).
The shape is \((s_0, s_1, ..., s_{P-1})\), where \(P \ge 1\).
indices has shape \((i_0, i_1, ..., i_{Q-2}, N)\), where \(Q \ge 2\) and \(N \le P\).
The last dimension of indices (with length \(N\) ) indicates slices along the \(N\) th dimension of the empty tensor.
updates is a tensor of rank \(Q-1+P-N\), and its shape is \((i_0, i_1, ..., i_{Q-2}, s_N, s_{N+1}, ..., s_{P-1})\).
If indices contains duplicates, the duplicate updates are summed.
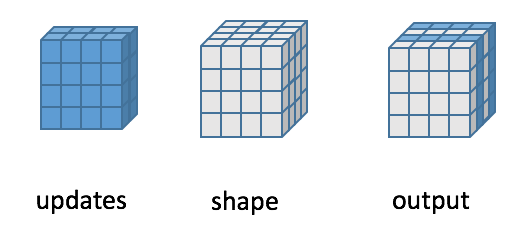
The following figure shows the calculation process of inserting two new value matrices into the first dimension with rank-3:
- Parameters
indices (Tensor) – The index of scattering in the new tensor. The rank of indices must be at least 2 and indices.shape[-1] <= len(shape).
updates (Tensor) – The source tensor to be updated. It has shape indices.shape[:-1] + shape[indices.shape[-1]:].
shape (tuple[int]) – The shape of the output tensor. shape can not be empty, and the elements in shape must be greater than or equal to 1.
- Returns
Tensor
- Supported Platforms:
AscendGPUCPU
Examples
>>> import mindspore >>> indices = mindspore.tensor([[0], [2]], mindspore.int32) >>> updates = mindspore.tensor([[[1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2], ... [3, 3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4, 4]], ... [[1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2], ... [3, 3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4, 4]]], mindspore.float32) >>> shape = (4, 4, 4) >>> output = mindspore.ops.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape) >>> print(output) [[[1. 1. 1. 1.] [2. 2. 2. 2.] [3. 3. 3. 3.] [4. 4. 4. 4.]] [[0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.]] [[1. 1. 1. 1.] [2. 2. 2. 2.] [3. 3. 3. 3.] [4. 4. 4. 4.]] [[0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.] [0. 0. 0. 0.]]] >>> indices = mindspore.tensor([[0, 1], [1, 1]], mindspore.int32) >>> updates = mindspore.tensor([3.2, 1.1], mindspore.float32) >>> shape = (3, 3) >>> output = mindspore.ops.scatter_nd(indices, updates, shape) >>> # In order to facilitate understanding, explain the operator pseudo-operation process step by step: >>> # Step 1: Generate an empty Tensor of the specified shape according to the shape >>> # [ >>> # [0. 0. 0.] >>> # [0. 0. 0.] >>> # [0. 0. 0.] >>> # ] >>> # Step 2: Modify the data at the specified location according to the indicators >>> # 0th row of indices is [0, 1], 0th row of updates is 3.2. >>> # means that the empty tensor in the 0th row and 1st col set to 3.2 >>> # [ >>> # [0. 3.2. 0.] >>> # [0. 0. 0.] >>> # [0. 0. 0.] >>> # ] >>> # 1th row of indices is [1, 1], 1th row of updates is 1.1. >>> # means that the empty tensor in the 1th row and 1st col set to 1.1 >>> # [ >>> # [0. 3.2. 0.] >>> # [0. 1.1 0.] >>> # [0. 0. 0.] >>> # ] >>> # The final result is as follows: >>> print(output) [[0. 3.2 0.] [0. 1.1 0.] [0. 0. 0.]]