重计算
概述
MindSpore采用反向模式的自动微分,根据正向图计算流程来自动推导出反向图,正向图和反向图一起构成了完整的计算图。在计算某些反向算子时,需要用到一些正向算子的计算结果,导致这些正向算子的计算结果需要驻留在内存中,直到依赖它们的反向算子计算完,这些正向算子的计算结果占用的内存才会被复用。这一现象推高了训练的内存峰值,在大规模网络模型中尤为显著。
为了解决这个问题,MindSpore提供了重计算的功能,可以不保存正向算子的计算结果,让这些内存可以被复用,然后在计算反向算子时,如果需要正向的结果,再重新计算正向算子。此教程以模型ResNet-50为例,讲解MindSpore如何配置重计算功能去训练模型。
相关接口:
mindspore.nn.Cell.recompute():调用Cell的recompute接口,调用该接口之后,在计算反向部分时,除了该Cell的输出算子,Cell里面其他的所有算子以及子Cell里面的所有算子都会被重新计算。PyNative模式和Graph模式都支持。mindspore.ops.Primitive.recompute():调用Primitive的recompute接口,调用该接口之后,在计算反向部分时,该算子会被重新计算。只支持Graph模式。mindspore.recompute():调用mindspore的recompute接口,调用该接口之后,网络模块会被重新计算。只支持PyNative模式。
基本原理
MindSpore根据正向图计算流程来自动推导出反向图,正向图和反向图一起构成了完整的计算图。在计算某些反向算子时,可能需要用到某些正向算子的计算结果,导致这些正向算子的计算结果,需要驻留在内存中直到这些反向算子计算完,它们所占的内存才会被其他算子复用。而这些正向算子的计算结果,长时间驻留在内存中,会推高计算的内存占用峰值,在大规模网络模型中尤为显著。
为了降低内存峰值,重计算技术可以不保存正向激活层的计算结果,让该内存可以被复用,然后在计算反向部分时,重新计算出正向激活层的结果。MindSpore提供了重计算的能力。
重计算功能具体实现为根据用户指定的需要做重计算的正向算子,复制出一份相同的算子,输出到反向算子上,并删除原正向算子与反向算子间的连边关系。另外,我们需要保证复制出来的算子,在计算相应的反向部分时才开始被计算,所以需要插入控制依赖去保证算子执行顺序。如下图所示:
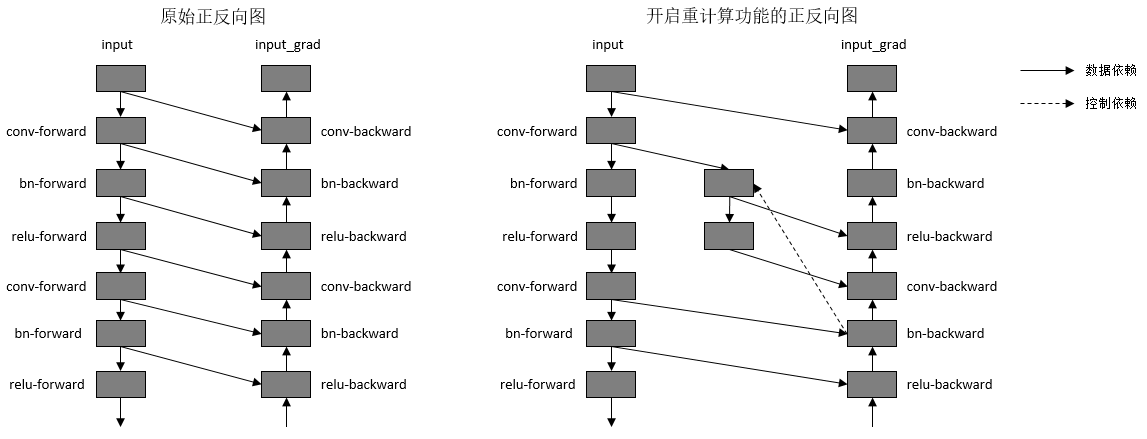
图:开启重计算功能前后的正反向示意图
为了方便用户使用,MindSpore目前不仅提供了针对单个算子设置的重计算接口,还提供针对Cell设置的重计算接口。当用户调用Cell的重计算接口时,这个Cell里面的所有正向算子都会被设置为重计算。
以GPT-3模型为例,设置策略为对每层layer对应的Cell设置为重计算,然后每层layer的输出算子设置为非重计算。72层GPT-3网络开启重计算的效果如下图所示:
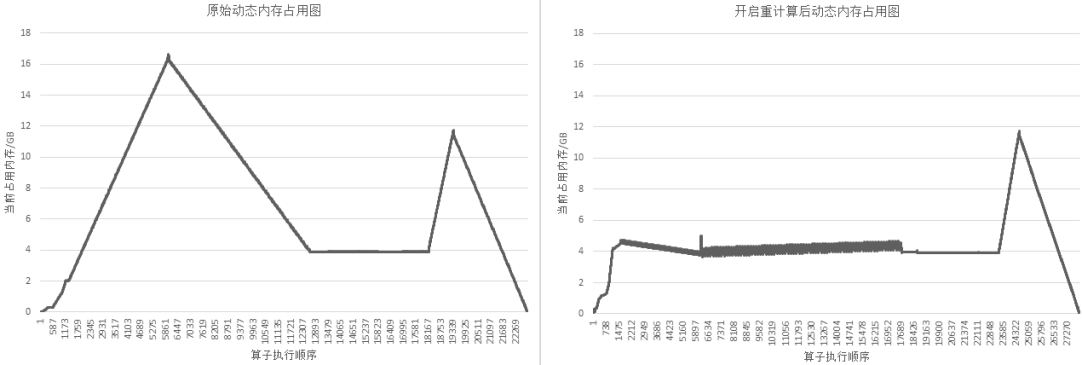
图:开启重计算功能前后的GPT-3内存使用比较
操作实践
下面以Ascend为例,进行重计算操作说明:
样例代码说明
下载完整的样例代码:recompute。
目录结构如下:
└─ sample_code
├─ recompute
└── example.py
...
其中,example.py是定义网络结构和执行流程的脚本。为了对比重计算开启前后的差异,该样例默认未开启重计算,如需开启请参考下文配置。
网络定义
网络Net由nn.CellList中的10个子网络Block依次连接而成,Grad用于对Net进行求导,得到关于网络输入的导数。
import numpy as np
from mindspore.nn import Cell
from mindspore.common import Tensor, Parameter
from mindspore import ops, nn
class Block(Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.transpose1 = ops.Transpose()
self.transpose2 = ops.Transpose()
self.transpose3 = ops.Transpose()
self.transpose4 = ops.Transpose()
self.real_div1 = ops.RealDiv()
self.real_div2 = ops.RealDiv()
self.batch_matmul1 = ops.BatchMatMul()
self.batch_matmul2 = ops.BatchMatMul()
self.add = ops.Add()
self.softmax = ops.Softmax(-1)
self.dropout = ops.Dropout(0.9)
self.expand_dims = ops.ExpandDims()
self.sub = ops.Sub()
self.mul = ops.Mul()
self.y = Parameter(Tensor(np.ones((8, 128, 128)).astype(np.float32)))
def construct(self, x):
transpose1 = self.transpose1(x, (0, 2, 1, 3))
real_div1 = self.real_div1(transpose1, Tensor(2.37891))
transpose2 = self.transpose2(x, (0, 2, 3, 1))
real_div2 = self.real_div2(transpose2, Tensor(2.37891))
batch_matmul1 = self.batch_matmul1(real_div1, real_div2)
expand_dims = self.expand_dims(self.y, 1)
sub = self.sub(Tensor([1.0]), expand_dims)
mul = self.mul(sub, Tensor([-0.0001]))
add = self.add(mul, batch_matmul1)
soft_max = self.softmax(add)
dropout = self.dropout(soft_max)
transpose3 = self.transpose3(x, (0, 2, 1, 3))
batch_matmul2 = self.batch_matmul2(dropout[0], transpose3)
transpose4 = self.transpose4(batch_matmul2, (0, 2, 1, 3))
return transpose4
class Net(Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.blocks = nn.CellList()
for _ in range(10):
b = Block()
self.blocks.append(b)
def construct(self, x):
out = x
for i in range(10):
out = self.blocks[i](out)
return out
class Grad(Cell):
def __init__(self, net):
super(Grad, self).__init__()
self.grad = ops.GradOperation()
self.net = net
def construct(self, x):
grad_net = self.grad(self.net)
return grad_net(x)
执行网络
在这一步,我们需要定义网络输入,然后调用Grad以获取导数,代码如下:
import numpy as np
from mindspore.common import Tensor
input_x = Tensor(np.ones((8, 128, 16, 32)).astype(np.float32))
network = Net()
grad_network = Grad(network)
output = grad_network(input_x)
print(output)
运行脚本
接下来通过命令调用对应的脚本,如下所示:
GLOG_v=1 python example.py
通过GLOG_v=1命令,我们可以打印出INFO级别的日志,从而查看网络执行内存占用大小,如下所示:
Device MOC memory size: 32768M
MindSpore Used memory size: 30682M
MindSpore memory base address: 0x12c100000000
Total Static Memory size: 1032M
Total Dynamic memory size: 167M
Actual peak memory usage: 1199M
Dynamic memory size of this graph: 0M
可以看到执行该网络的动态内存占用大小为167 MB。如果我们在执行脚本前,设置环境变量export MS_DEV_SAVE_GRAPHS=1,可以看到在执行脚本的目录下,会生成xx_validate_xxx.ir文件。打开xx_validate_xxx.ir文件,如下所示,我们可以看到节点%38的计算结果,需要供节点%41(正向传播算子)和节点%291(反向传播算子)计算时使用,所以节点%38的计算结果占用的内存,需要等到节点%291计算完成,才会被释放掉(此处%后面的序号与算子执行序相关)。节点%38计算结果的内存占用时间长的原因是,反向传播的顺序与正向传播相反,正向传播中的10个Block里面,第一个Block对应的反向传播函数反而是最后执行的。
%38(equiv_11_real_div1) = PrimFunc_RealDiv(%37, Tensor(shape=[], dtype=Float32, value=2.37891)) {instance name: real_div2} cnode_attrs: {checkpoint: Bool(1)} cnode_primal_attrs: {unique_id: "10058"}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (), value=...>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>)
# Fullname with scope: (Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/RealDiv-op0)
...
%41(equiv_8_batch_matmul1) = PrimFunc_BatchMatMul(%38, %40, Bool(0), Bool(0)) cnode_attrs: {checkpoint: Bool(1)} cnode_primal_attrs: {unique_id: "10055"}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 32, 128)>, <Bool, NoShape>, <Bool, NoShape>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 128)>)
# Fullname with scope: (Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/BatchMatMul-op0)
...
%291(CNode_401) = PrimFunc_BatchMatMul(%38, %287, Bool(1), Bool(0)) cnode_attrs: {checkpoint: Bool(1)} cnode_primal_attrs: {forward_node_name: "BatchMatMul_10055", forward_unique_id: "10055"}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 128)>, <Bool, NoShape>, <Bool, NoShape>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 32, 128)>)
# Fullname with scope: (Gradients/Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/Grad_BatchMatMul/BatchMatMul-op38)
如果我们对第一个Block做重计算,那么就可以使得第一个Block在正向部分计算结束后,计算结果立即被释放掉,在反向传播时才去重新计算,从而可以显著缩短内存占用的时间,降低内存峰值。使用重计算的代码如下:
class Net(Cell):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.blocks = nn.CellList()
for _ in range(10):
b = Block()
# 对每个Block调用recompute接口来开启重计算功能
b.recompute()
self.blocks.append(b)
def construct(self, x):
out = x
for i in range(10):
out = self.blocks[i](out)
return out
使用重计算后,我们再运行脚本,如下所示:
GLOG_v=1 python example.py
再次查看网络执行内存占用大小,如下所示,执行该网络的动态内存占用减少为69 MB。
Device MOC memory size: 32768M
MindSpore Used memory size: 30680M
MindSpore memory base address: 0x12c100000000
Total Static Memory size: 1032M
Total Dynamic memory size: 69M
Actual peak memory usage: 1101M
Dynamic memory size of this graph: 0M
再次打开xx_validate_xxx.ir文件,如下所示,可以看到反向传播节点%429的第一个输入为节点%416,节点%416是根据正向传播节点%38复制得到的,而节点%38的计算结果占用的内存,在节点%41计算完后就可以被释放,从而提高了内存复用率。
%38(equiv_93_real_div1) = PrimFunc_RealDiv(%37, Tensor(shape=[], dtype=Float32, value=2.37891)) {instance name: real_div2} cnode_attrs: {recompute_sub_graph: U64(0), recompute_id: I64(5), recompute: Bool(1), need_cse_after_recompute: Bool(1)} cnode_primal_attrs: {unique_id: "13860"}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (), value=...>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>)
# Fullname with scope: (recompute_Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/RealDiv-op0)
...
%41(equiv_90_batch_matmul1) = PrimFunc_BatchMatMul(%38, %40, Bool(0), Bool(0)) {instance name: batch_matmul2} cnode_attrs: {recompute_sub_graph: U64(0), recompute_id: I64(8), recompute: Bool(1), need_cse_after_recompute: Bool(1)} cnode_primal_attrs: {unique_id: "13857"}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 32, 128)>, <Bool, NoShape>, <Bool, NoShape>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 128)>)
# Fullname with scope: (recompute_Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/BatchMatMul-op0)
...
%416(CNode_1062) = PrimFunc_RealDiv(%410, Tensor(shape=[], dtype=Float32, value=2.37891)) {instance name: real_div2} cnode_attrs: {recompute_sub_graph: U64(0), recompute_id: I64(5), duplicated: Bool(1), need_cse_after_recompute: Bool(1)}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (), value=...>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>)
# Fullname with scope: (recompute_Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/RealDiv-op2)
...
%429(CNode_1075) = PrimFunc_BatchMatMul(%416, %425, Bool(1), Bool(0)) {instance name: batch_matmul2} cnode_attrs: {recompute_sub_graph: U64(0), target_grad: Bool(1), checkpoint: Bool(1)} cnode_primal_attrs: {forward_node_name: "BatchMatMul_13857", forward_unique_id: "13857"}
: (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 32)>, <Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 128, 128)>, <Bool, NoShape>, <Bool, NoShape>) -> (<Tensor[Float32], (8, 16, 32, 128)>)
# Fullname with scope: (Gradients/recompute_Default/net-Net/blocks-CellList/0-Block/Grad_BatchMatMul/BatchMatMul-op38)