Experiencing the Python Simplified Concurrent Inference Demo
Overview
This tutorial provides a sample program for MindSpore Lite to perform concurrent inference. By creating concurrent inference configuration, loading and compiling concurrent Runner, setting concurrent inference task, and executing concurrent inference, it demonstrates the basic process of Python interface for server-side concurrent inference, so that users can quickly understand the use of MindSpore Lite to perform concurrent inference-related APIs. The related code is located in mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python directory.
The usage scenario simulated by this tutorial: When the server receives inference tasks requested by multiple clients at the same time, it uses the ModelParallelRunner interface that supports concurrent inference. Multiple inference tasks are performed at the same time and the results are returned to the client.
The following is an example of how to use the Python simplified concurrent inference demo on a Linux X86 operating system and a CPU hardware platform, taking Ubuntu 18.04 as an example.
One-click installation of inference-related model files, MindSpore Lite and its required dependencies. See the One-click installation section for details.
Execute the Python Simplified Inference Demo. See the Execute Demo section for details.
For a description of the Python Simplified Inference Demo content, see the Demo Content Description section for details.
One-click Installation
This session introduces the installation of MindSpore Lite for Python version 3.7 via pip on a Linux-x86_64 system with a CPU environment, taking the new Ubuntu 18.04 as an example.
Go to mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python directory, and execute the lite-server-cpu-pip.sh script to install in one click, taking MindSpore Lite version 1.9.0 as an example. The installation script downloads the model and input data files required for concurrent inference, installs the dependencies required for MindSpore_Lite, and downloads and installs MindSpore Lite that supports concurrent inference.
Note: This command sets the installed version of MindSpore Lite. Since the Python interface is supported from MindSpore Lite version 1.8.0, the version cannot be set lower than 1.8.0. For the versions that can be set, see the version provided in Download MindSpore Lite for details.
MINDSPORE_LITE_VERSION=1.9.0 bash ./lite-server-cpu-pip.sh
If the MobileNetV2 model download fails, please manually download the relevant model file mobilenetv2.ms and copy it to the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python/modeldirectory.If the input.bin input data files download fails, please manually download the relevant model file input.bin and copy it to the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python/modeldirectory.If you fail to download MindSpore Lite Concurrent Inference Framework by using the script, please manually download MindSpore Lite Concurrent Model Inference Framework for the corresponding hardware platform of CPU and operating system of Linux-x86_64 or MindSpore Lite Concurrent Model Inference Framework for the corresponding hardware platform of CPU and operating system of Linux-aarch64. Users can use the
uname -mcommand to query the operating system on the terminal, and copy it tomindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_pythondirectory.If you need to use MindSpore Lite corresponding to Python 3.7 or above, please compile locally, noting that the Python API module compilation depends on Python >= 3.7.0, NumPy >= 1.17.0, wheel >= 0.32.0. It should be noted that to generate a MindSpore Lite installation package that supports concurrent inference, and you need to configure the environment variable before compiling: export MSLITE_ENABLE_SERVER_INFERENCE=on. After successful compilation, copy the Whl installation package generated in the
output/directory to themindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_pythondirectory.If the MindSpore Lite installation package does not exist in the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_pythondirectory, the one-click installation script will uninstall the currently installed MindSpore Lite and then download and install MindSpore Lite from the Huawei image. Otherwise, if the MindSpore Lite installation package exists in the directory, it will install it first.After manually downloading and placing the files in the specified directory, you need to execute the lite-server-cpu-pip.sh script again to complete the one-click installation.
A successful execution will show the following results. The model files and input data files can be found in the mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python/model directory.
Successfully installed mindspore-lite-1.9.0
Executing Demo
After one-click installation, go to the [mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python](https://gitee.com/mindspore/mindspore/tree/r2.0.0-alpha/mindspore/ lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_python) directory and execute the following command to experience the MindSpore Lite concurrent inference MobileNetV2 model.
python quick_start_server_inferece_python.py
The following results will be obtained when the execution is completed. During the execution of concurrent inference tasks in multiple threads, the single time-consuming inference and inference results in concurrent inference are printed, and the total concurrent inference time-consuming is printed after ending the thread.
Description of inference results:
Simulates 5 clients and sends concurrent inference task requests to the server at the same time, with
parallel iddenoting the client id.Simulates each client to send 2 requests for inference tasks to the server, and
task indexdenotes the serial number of the task.run once timeindicates the inference time for a single requested inference task per client.Next, the inference results of each client for single requested inference task are displayed, including the name of the output Tensor, the data size of the output Tensor, the number of elements of the output Tensor, and the first 5 pieces of data.
total run timeindicates the total time taken by the server to complete all concurrent inference tasks.parallel id: 0 | task index: 1 | run once time: 0.024082660675048828 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 2 | task index: 1 | run once time: 0.029989957809448242 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 1 | task index: 1 | run once time: 0.03409552574157715 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 3 | task index: 1 | run once time: 0.04005265235900879 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 4 | task index: 1 | run once time: 0.04981422424316406 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 0 | task index: 2 | run once time: 0.028667926788330078 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 2 | task index: 2 | run once time: 0.03010392189025879 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 3 | task index: 2 | run once time: 0.030695676803588867 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 1 | task index: 2 | run once time: 0.04117941856384277 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 parallel id: 4 | task index: 2 | run once time: 0.028671741485595703 s tensor name is:Softmax-65 tensor size is:4004 tensor elements num is:1001 output data is: 1.02271215e-05 9.92699e-06 1.6968432e-05 6.8573616e-05 9.731416e-05 total run time: 0.08787751197814941 s
Demo Content Description
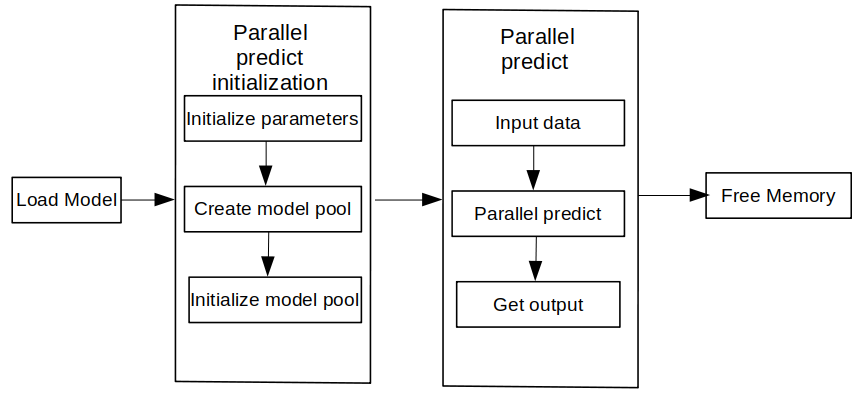
Performing concurrent inference with MindSpore Lite consists of the following main steps:
key variable description: Description of the key variables used in concurrent inference.
Create concurrent inference configuration: Create the concurrent inference configuration option RunnerConfig to save some basic configuration parameters used to perform the initialization of concurrent inference.
Concurrent Runner loading and compilation: Before performing concurrent inference, you need to call init interface of
ModelParallelRunnerfor concurrent Runner initialization, mainly for model reading, loadingRunnerConfigconfiguration, creating concurrency, and subgraph slicing and operator selection scheduling. TheModelParallelRunnercan be understood as amodelthat supports concurrent inference. This phase can take more time, so it is recommended thatModelParallelRunnerbe initialized once and perform concurrent inference multiple times.Set concurrent inference task: Create multiple threads and bind concurrent inference tasks. The inference tasks include populating the
Input Tensorwith data, using the predict interface ofModelParallelRunnerfor concurrent inference and getting inference results via theoutput Tensor.perform concurrent inference: Start multiple threads and execute the configured concurrent inference tasks. During execution, the single inference time consumption and inference result in concurrent inference are printed, and the total concurrent inference time consumption is printed after the end of the thread.
For more advanced usage and examples of Python interfaces, please refer to the Python API.
Key Variable Description
THREAD_NUM: the number of threads in a single worker.WORKERS_NUM * THREAD_NUMshould be less than the number of machine cores.WORKERS_NUM: On the server side, specify the number of workers in aModelParallelRunner, i.e., the units that perform concurrent inference. If you want to compare the difference in inference time between concurrent inference and non-concurrent inference, you can setWORKERS_NUMto 1 for comparison.PARALLEL_NUM: The number of concurrent, i.e., the number of clients that are sending inference task requests at the same time.TASK_NUM: The number of tasks, i.e., the number of inference task requests sent by a single client.import time from threading import Thread import numpy as np import mindspore_lite as mslite # the number of threads of one worker. # WORKERS_NUM * THREAD_NUM should not exceed the number of cores of the machine. THREAD_NUM = 1 # In parallel inference, the number of workers in one `ModelParallelRunner` in server. # If you prepare to compare the time difference between parallel inference and serial inference, # you can set WORKERS_NUM = 1 as serial inference. WORKERS_NUM = 3 # Simulate 5 clients, and each client sends 2 inference tasks to the server at the same time. PARALLEL_NUM = 5 TASK_NUM = 2
Creating Concurrent Inference Configuration
Create concurrent inference configuration RunnerConfig. Since this tutorial demonstrates a scenario where inference is performed on a CPU device, it is necessary to add the created CPU device hardware information to the context Conterxt and then add Conterxt to RunnerConfig.
# Init RunnerConfig and context, and add CPU device info
cpu_device_info = mslite.CPUDeviceInfo(enable_fp16=False)
context = mslite.Context(thread_num=THREAD_NUM, inter_op_parallel_num=THREAD_NUM)
context.append_device_info(cpu_device_info)
parallel_runner_config = mslite.RunnerConfig(context=context, workers_num=WORKERS_NUM)
Concurrent Runner Loading and Compilation
Call init interface of ModelParallelRunner for concurrent Runner initialization, mainly for model reading, loading RunnerConfig configuration, creating concurrency, and subgraph slicing and operator selection scheduling. The ModelParallelRunner can be understood as a Model that supports concurrent inference. This phase can take more time, so it is recommended that ModelParallelRunner be initialized once and perform concurrent inference multiple times.
# Build ModelParallelRunner from file
model_parallel_runner = mslite.ModelParallelRunner()
model_parallel_runner.init(model_path="./model/mobilenetv2.ms", runner_config=parallel_runner_config)
Setting Concurrent Inference Task
Create multiple threads and bind concurrent inference tasks. The inference tasks include populating the Input Tensor with data, using the predict interface of ModelParallelRunner for concurrent inference and getting inference results via the output Tensor.
def parallel_runner_predict(parallel_runner, parallel_id):
"""
One Runner with 3 workers, set model input, execute inference and get output.
Args:
parallel_runner (mindspore_lite.ModelParallelRunner): Actuator Supporting Parallel inference.
parallel_id (int): Simulate which client's task to process
"""
task_index = 0
while True:
if task_index == TASK_NUM:
break
task_index += 1
# Set model input
inputs = parallel_runner.get_inputs()
in_data = np.fromfile("./model/input.bin", dtype=np.float32)
inputs[0].set_data_from_numpy(in_data)
once_start_time = time.time()
# Execute inference
outputs = []
parallel_runner.predict(inputs, outputs)
once_end_time = time.time()
print("parallel id: ", parallel_id, " | task index: ", task_index, " | run once time: ",
once_end_time - once_start_time, " s")
# Get output
for output in outputs:
tensor_name = output.get_tensor_name().rstrip()
data_size = output.get_data_size()
element_num = output.get_element_num()
print("tensor name is:%s tensor size is:%s tensor elements num is:%s" % (tensor_name, data_size,
element_num))
data = output.get_data_to_numpy()
data = data.flatten()
print("output data is:", end=" ")
for j in range(5):
print(data[j], end=" ")
print("")
# The server creates 5 threads to store the inference tasks of 5 clients.
threads = []
total_start_time = time.time()
for i in range(PARALLEL_NUM):
threads.append(Thread(target=parallel_runner_predict, args=(model_parallel_runner, i,)))
Performing Concurrent Inference
Start multiple threads and execute the configured concurrent inference tasks. During execution, the single inference time consumption and inference result in concurrent inference are printed, and the total concurrent inference time consumption is printed after the end of the thread.
# Start threads to perform parallel inference.
for th in threads:
th.start()
for th in threads:
th.join()
total_end_time = time.time()
print("total run time: ", total_end_time - total_start_time, " s")
