Experience Java Minimalist Concurrent Reasoning Demo
Overview
This tutorial provides an example program for MindSpore Lite to parallel inference. It demonstrates the basic process of performing inference on the device side using MindSpore Lite Java API by random inputting data, executing inference, and printing the inference result. You can quickly understand how to use the Java APIs related to inference on MindSpore Lite. In this tutorial, the randomly generated data is used as the input data to perform the inference on the MobileNetV2 model and print the output data. The code is stored in the mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_java directory.
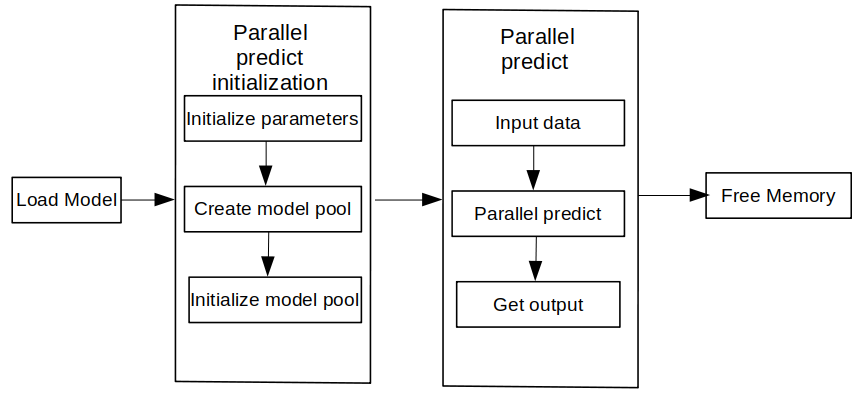
The MindSpore Lite inference steps are as follows:
Load the model: Read the
.msmodel converted by the model conversion tool from the file system.Create and configure context: Create a configuration RunnerConfig to save some basic configuration parameters required by a ModelParallelRunner to guide model pool init. including
MSContext,threadNum(number of threads),WorkersNum.Init: Before building a graph, the ModelParallelRunner interface of init needs to be called to init the model parallel runner, including init model pool and subgraph partition and operator selection and scheduling. This takes a long time. Therefore, it is recommended that with one Init created, one graph be built. In this case, the inference will be performed for multiple times.
Input data: Before the graph is executed, data needs to be filled in the
Input Tensor.Perform inference: Use the predict of the ModelParallelRunner to perform model inference.
Obtain the output: After the graph execution is complete, you can obtain the inference result by
outputting the tensor.Release the memory: If the MindSpore Lite inference framework is not required, release the created ModelParallelRunner.
Building and Running
Environment requirements
Build
Run the build script in the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_javadirectory to automatically download the MindSpore Lite inference framework library and model files and build the Demo.bash build.shIf the MindSpore Lite inference framework fails to be downloaded, manually download the MindSpore Lite model inference framework mindspore-lite-{version}-linux-x64.tar.gz whose hardware platform is CPU and operating system is Ubuntu-x64. Decompress the package and copy
runtime/lib/mindspore-lite-java.jarfile to themindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_java/libdirectory.If the MobileNetV2 model fails to be downloaded, manually download the model file mobilenetv2.ms and copy it to the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_java/model/directory.After manually downloading and placing the file in the specified location, you need to execute the build.sh script again to complete the compilation.
Inference
After the build, go to the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_server_inference_java/targetdirectory and run the following command to experience MindSpore Lite inference on the MobileNetV2 model:java -classpath .:./quick_start_server_inference_java.jar:../lib/mindspore-lite-java.jar com.mindspore.lite.demo.Main ../model/mobilenetv2.ms
After the execution, the following information is displayed:
========== model parallel runner predict success ==========
Init
ModelParallelRunner Init includes context configuration creation and model compilation.
private static ModelParallelRunner runner;
private static List<MSTensor> inputs;
private static List<MSTensor> outputs;
// use default param init context
MSContext context = new MSContext();
context.init(1,0);
boolean ret = context.addDeviceInfo(DeviceType.DT_CPU, false, 0);
if (!ret) {
System.err.println("init context failed");
context.free();
return ;
}
// init runner config
RunnerConfig config = new RunnerConfig();
config.init(context);
config.setWorkersNum(2);
// init ModelParallelRunner
ModelParallelRunner runner = new ModelParallelRunner();
ret = runner.init(modelPath, config);
if (!ret) {
System.err.println("ModelParallelRunner init failed.");
runner.free();
return;
}
Parallel predict
Model inference includes data input, inference execution, and output obtaining. In this example, the input data is randomly generated, and the output result is printed after inference.
// init input tensor
inputs = new ArrayList<>();
MSTensor input = runner.getInputs().get(0);
if (input.getDataType() != DataType.kNumberTypeFloat32) {
System.err.println("Input tensor data type is not float, the data type is " + input.getDataType());
return;
}
// Generator Random Data.
int elementNums = input.elementsNum();
float[] randomData = generateArray(elementNums);
ByteBuffer inputData = floatArrayToByteBuffer(randomData);
// create input MSTensor
MSTensor inputTensor = MSTensor.createTensor(input.tensorName(), DataType.kNumberTypeFloat32,input.getShape(), inputData);
inputs.add(inputTensor);
// init output
outputs = new ArrayList<>();
// runner do predict
ret = runner.predict(inputs,outputs);
if (!ret) {
System.err.println("MindSpore Lite predict failed.");
freeTensor();
runner.free();
return;
}
System.out.println("========== model parallel runner predict success ==========");
Memory Release
If the MindSpore Lite inference framework is not required, release the created ModelParallelRunner.
private static void freeTensor(){
for (int i = 0; i < inputs.size(); i++) {
inputs.get(i).free();
}
for (int i = 0; i < outputs.size(); i++) {
outputs.get(i).free();
}
}
freeTensor();
runner.free();
