Overview of Post-training Quantization Algorithms
This article introduces some basic concepts of quantization algorithms before introducing specific quantization algorithms to help users understand them. If you already have a deeper understanding of quantization algorithms, you can directly jump to the Examples subsection.
Background
With the development of deep learning, neural networks are widely used in a variety of fields, and the increase in network accuracy also introduces a huge number of parameters and computation. At the same time more and more applications choose to use deep learning techniques on mobile devices or edge devices.
In the case of cell phones, for example, operating systems and APP applications are beginning to integrate AI functionality in order to provide humanized and intelligent services. Using this function, it is inevitable to introduce network files and weight files into the cell phone software. Taking the classic AlexNet as an example, the original weight file has exceeded 200MB, and the new networks that have emerged recently are moving towards a more complex structure with more parameters.
Due to the limited hardware resources of mobile devices and edge devices, there is a need to streamline the network, and Quantization is one of the techniques derived to cope with this type of problem. Network quantization is a technique for converting floating-point computations into low-ratio specific-point computations, which can effectively reduce network computation, parameter sizes, and memory consumption, but tends to introduce some loss of precision.
Quantization Method
Quantization is the process of approximating a 32-bit finite-range floating-point type (FP32) weight or activation in a network to a finite number of discrete values (usually int8) with a low loss of inference accuracy. In other words, it is the process of approximating the representation of FP32 data with fewer bits of data types, while the inputs and outputs of the network remain floating-point, thus achieving the goals of reducing the size of the network dimensions, decreasing the memory consumption when the network is deployed, and speeding up the network inference.
Although quantization will lose accuracy because quantization is equivalent to introducing noise to the network, neural networks are generally less sensitive to noise, as long as the degree of quantization is well controlled, the impact on the accuracy of high-level tasks can be very small. Compared with the original network, the performance of the quantized network can be greatly improved by replacing the original FP32 computation with INT8 operation in the network inference.
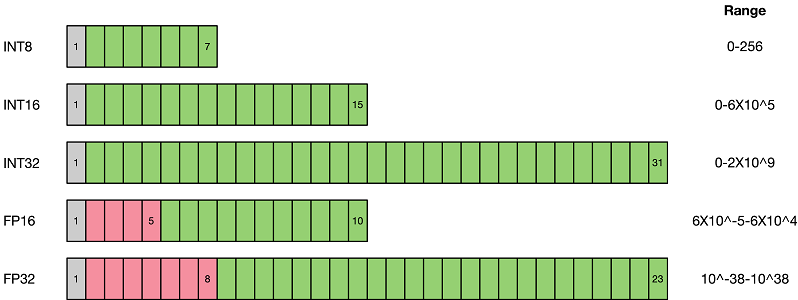
As shown above, low-precision data expression types such as FP16 and INT8 take up less space compared to FP32 types. Replacing high-precision data expression types with low-precision data expression types can significantly reduce storage space and transmission time. The inference performance of low bits is also higher, and the acceleration ratio of INT8 relative to FP32 can be 3 times or even higher. For the same computation, there is also a significant advantage in power consumption.
Currently, there are two main types of quantization schemes in the industry: Quantization Aware Training and Post-training Quantization.
Quantization Aware Training requires training data and usually performs better in terms of network accuracy, and is suitable for scenarios that require high network compression rate and network accuracy. The purpose is to reduce the loss of accuracy, and its participation in the forward inference process of network training allows the network to obtain the difference of the quantization loss, but the gradient update needs to be performed in floating point, thus it does not participate in the back propagation process.
Post-training Quantization is simple to use and requires only a small amount of calibration data, making it suitable for scenarios that seek high ease of use and lack training resources.
This chapter contains some post-training quantization algorithms, and quantization-aware training can be found in Quantization-aware training chapter
Examples
PTQ algorithm examples: a post-quantization algorithm built on MindSpore dynamic graph capabilities, supporting weight quantization, full quantization, and KVCache quantization.
RTN algorithm examples: a MinMax-based basic post-quantization algorithm that supports only 8bit weight quantization and 8bit KVCache quantization.