Implementing an Image Classification Application of Cross-device Federated Learning (x86)
Federated learning can be divided into cross-silo federated learning and cross-device federated learning according to different participating customers. In the cross-silo federation learning scenario, the customers participating in federated learning are different organizations (for example, medical or financial) or geographically distributed data centers, that is, training models on multiple data islands. The clients participating in the cross-device federation learning scenario are a large number of mobiles or IoT devices. This framework will introduce how to use the network LeNet to implement an image classification application on the MindSpore cross-silo federation framework, and provides related tutorials for simulating to start multi-client participation in federated learning in the x86 environment.
Before you start, check whether MindSpore has been correctly installed. If not, install MindSpore on your computer by referring to Install on the MindSpore website.
Preparatory Work
We provide Federated Learning Image Classification Dataset FEMNIST and the device-side model file of the .ms format for users to use directly. Users can also refer to the following tutorials to generate the datasets and models based on actual needs.
Data Processing
In this example, the federated learning dataset FEMNIST in the leaf dataset is used. For the specific acquisition method of the dataset, please refer to the document Device-cloud federation learning image classification dataset processing.
Users can also define the dataset by themselves. Note that the dataset must be a .bin format file, and the data dimension in the file must be consistent with the input dimension of the network.
Generating a Device Model File
Define the network and training process
For the definition of the specific network and training process, please refer to Beginners Getting Started.
We provide the network definition file model.py and the training process definition file run_export_lenet.py for your reference.
Export a model as a MindIR file.
Run the script
run_export_lenet.pyto obtain the MindIR format model file, the code snippet is as follows:from mindspore import export ... parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="export mindir for lenet") parser.add_argument("--device_target", type=str, default="CPU") parser.add_argument("--mindir_path", type=str, default="lenet_train.mindir") # The path for the file in MindIR format. ... for _ in range(epoch): data = Tensor(np.random.rand(32, 3, 32, 32).astype(np.float32)) label = Tensor(np.random.randint(0, 61, (32)).astype(np.int32)) loss = train_network(data, label).asnumpy() losses.append(loss) export(train_network, data, label, file_name= mindir_path, file_format='MINDIR') # Add the export statement to obtain the model file in MindIR format. print(losses)
The specific operating instructions are as follows:
python run_export_lenet.py --mindir_path="ms/lenet/lenet_train.mindir"
The parameter
--mindir_pathis used to set the path of the generated file in MindIR format.Convert the MindIR file into an .ms file that can be used by the federated learning framework on the device.
For details about model conversion, see Training Model Conversion Tutorial.
The following is an example of model conversion:
Assume that the model file to be converted is
lenet_train.mindir. Run the following command:./converter_lite --fmk=MINDIR --trainModel=true --modelFile=lenet_train.mindir --outputFile=lenet_train
If the conversion is successful, the following information is displayed:
CONVERTER RESULT SUCCESS:0
This indicates that the MindSpore model is successfully converted to the MindSpore device model and the new file
lenet_train.msis generated. If the conversion fails, the following information is displayed:CONVERT RESULT FAILED:
Save the generated model file in
.msformat to a path. When the federated learning API is called, FLParameter.trainModelPath can be set to the path of the model file.
Simulating Multi-client Participation in Federated Learning
Prepare a model file for the client.
In the actual scenario, a client contains a model file in .ms format. In the simulation scenario, you need to copy multiple .ms files and name them in
lenet_train{i}.msformat. In the format, i indicates the client ID. Due to the script settings inrun.py, i must be set to a number, such as0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.... Each client uses an .ms file.You can copy and name the original .ms file by referring to the following steps:
import shutil import os def copy_file(raw_path,new_path,copy_num): # Copy the specified number of files from the raw path to the new path for i in range(copy_num): file_name = "lenet_train" + str(i) + ".ms" new_file_path = os.path.join(new_path, file_name) shutil.copy(raw_path ,new_file_path) print('====== copying ',i, ' file ======') print("the number of copy .ms files: ", len(os.listdir(new_path))) if __name__ == "__main__": raw_path = "lenet_train.ms" new_path = "ms/lenet" num = 8 copy_file(raw_path, new_path, num)
Set
raw_pathto the path of the original .ms file,new_pathto the path of the .ms file to be copied, andnumto the number of copies. Generally, you need to simulate the number of started clients.For example, in the preceding script, the .ms file is generated in the
ms/lenetdirectory for eight clients. The directory structure is as follows:ms/lenet ├── lenet_train0.ms # .ms file used by client 0. ├── lenet_train1.ms # .ms file used by client 1. ├── lenet_train2.ms # .ms file used by client 2. ├── lenet_train3.ms # .ms file used by client 3. │ │ ...... │ └── lenet_train7.ms # .ms file used by client 7.
Start the cloud side service
Users can first refer to cloud-side deployment tutorial to deploy the cloud-side environment and start the cloud-side service.
Start the client
Before starting the client, please refer to the section x86 in the Federated-Client deployment tutorial for deployment of device environment.
Our framework provides three types of federated learning interfaces for users to call. For specific interface introduction, please refer to API file :
SyncFLJob.flJobRun()Used to start the client to participate in the federated learning training task, and to obtain the final trained aggregation model.
SyncFLJob.modelInfer()Used to obtain the inference result of a given dataset.
SyncFLJob.getModel()Used to get the latest model on the cloud side.
After the cloud-side service starts successfully, you can write a Python script to call the federated learning framework jar package
mindspore-lite-java-flclient.jarand the jar package corresponding to the model scriptquick_start_flclient.jar(refer to Building a Package in the Federated-Client deployment tutorial) to simulate multi-client participation in federated learning tasks.We provide a reference script run_client_x86.py, users can set relevant parameters to start different federated learning interfaces.
Taking the LeNet network as an example, some of the input parameters in the
run_client_x86.pyscript have the following meanings, and users can set them according to the actual situation:--jarPathSpecifies the path of the JAR package of the federated learning framework. For details about how to obtain the JAR package in the x86 environment, see Building a Package in the Federated-Client deployment tutorial.
Note, please make sure that only the JAR package is included in the path. For example, in the above reference script,
--jarPathis set to"libs/jarX86/mindspore-lite-java-flclient.jar", you need to make sure that thejarX86folder contains only one JAR packagemindspore-lite-java-flclient.jar.--case_jarPathSpecifies the path of the JAR package
quick_start_flclient.jarcorresponding to the model script. For details about how to obtain the JAR package in the x86 environment, see Building a Package in the Federated-Client deployment tutorial.Note, please make sure that only the JAR package is included in the path. For example, in the above reference script,
--case_jarPathis set to"case_jar/quick_start_flclient.jar", you need to make sure that thecase_jarfolder contains only one JAR packagequick_start_flclient.jar.--train_datasetSpecifies the root path of the training dataset.The sentiment classification task stores the training data (in .txt format) of each client. The LeNet image classification task stores the training files data.bin and label.bin of each client, for example,
data/femnist/3500_clients_bin/.--flNameSpecifies the package path of model script used by federated learning. We provide two types of model scripts for your reference (Supervised sentiment classification task, Lenet image classification task). For supervised sentiment classification tasks, this parameter can be set to the package path of the provided script file AlBertClient.java, like as
com.mindspore.flclient.demo.albert.AlbertClient; for Lenet image classification tasks, this parameter can be set to the package path of the provided script file LenetClient.java, like ascom.mindspore.flclient.demo.lenet.LenetClient. At the same time, users can refer to these two types of model scripts, define the model script by themselves, and then set the parameter to the package path of the customized model file ModelClient.java (which needs to inherit from the class Client.java).--train_model_pathSpecifies the training model path used for federated learning. The path is the directory where multiple .ms files copied in the preceding tutorial are stored, for example,
ms/lenet. The path must be an absolute path.--train_ms_nameSet the same part of the multi-client training model file name. The model file name must be in the format
{train_ms_name}1.ms,{train_ms_name}2.ms,{train_ms_name}3.ms, etc.--domain_nameUsed to set the url for device-cloud communication. Currently, https and http communication are supported, the corresponding formats are like as: https://……, http://……, and when
if_use_elbis set to true, the format must be: https://127.0.0.1:6666 or http://127.0.0.1:6666 , where127.0.0.1corresponds to the ip of the machine providing cloud-side services (corresponding to the cloud-side parameter--scheduler_ip), and6666corresponds to the cloud-side parameter--fl_server_port.--taskSpecifies the type of the task to be started.
trainindicates that a training task is started.inferenceindicates that multiple data inference tasks are started.getModelindicates that the task for obtaining the cloud model is started. Other character strings indicate that the inference task of a single data record is started. The default value istrain. The initial model file (.ms file) is not trained. Therefore, you are advised to start the training task first. After the training is complete, start the inference task. (Note that the values of client_num in the two startups must be the same to ensure that the model file used byinferenceis the same as that used bytrain.)--batch_sizeSpecifies the number of single-step training samples used in federated learning training and inference, that is, batch size. It needs to be consistent with the batch size of the input data of the model.
--client_numSpecifies the number of clients. The value must be the same as that of
start_fl_job_cntwhen the server is started. This parameter is not required in actual scenarios.
If you want to know more about the meaning of other parameters in the
run_client_x86.pyscript, you can refer to the comments in the script.The basic startup instructions of the federated learning interface are as follows:
python run_client_x86.py --jarPath="libs/jarX86/mindspore-lite-java-flclient.jar" --case_jarPath="case_jar/quick_start_flclient.jar" --train_dataset="data/femnist/3500_clients_bin/" --test_dataset="null" --vocal_file="null" --ids_file="null" --flName="com.mindspore.flclient.demo.lenet.LenetClient" --train_model_path="ms/lenet/" --infer_model_path="ms/lenet/" --train_ms_name="lenet_train" --infer_ms_name="lenet_train" --domain_name="http://127.0.0.1:6666" --cert_path="certs/https_signature_certificate/client/CARoot.pem" --use_elb="true" --server_num=4 --client_num=8 --thread_num=1 --server_mode="FEDERATED_LEARNING" --batch_size=32 --task="train"
Note that the path-related parameters must give an absolute path.
The above commands indicate that eight clients are started to participate in federated learning. If the startup is successful, log files corresponding to the eight clients are generated in the current folder. You can view the log files to learn the running status of each client.
./ ├── client_0 │ └── client.log # Log file of client 0. │ ...... └── client_7 └── client.log # Log file of client 7.
For different interfaces and scenarios, you only need to modify specific parameter values according to the meaning of the parameters, such as:
Start federated learning and training tasks: SyncFLJob.flJobRun()
When
--taskinBasic Start Commandis set totrain, it means to start the task.You can use the command
grep -r "average loss:" client_0/client.logto view the average loss of each epoch ofclient_0during the training process. It will be printed as follows:INFO: <FLClient> ----------epoch:0,average loss:4.1258564 ---------- ......
You can also use the command
grep -r "evaluate acc:" client_0/client.logto view the verification accuracy of the model after the aggregation in each federated learning iteration forclient_0. It will be printed like the following:INFO: <FLClient> [evaluate] evaluate acc: 0.125 ......
Start the inference task: SyncFLJob.modelInference()
When
--taskinBasic Start Commandis set toinference, it means to start the task.You can view the inference result of
client_0through the commandgrep -r "the predicted labels:" client_0/client.log:INFO: <FLClient> [model inference] the predicted labels: [0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2] ......
Start the task of obtaining the latest model on the cloud side: SyncFLJob.getModel()
When
--taskinBasic Start Commandis set toinference, it means to start the task.If there is the following content in the log file, it means that the latest model on the cloud side is successfully obtained:
INFO: <FLClient> [getModel] get response from server ok!
Stop the client process.
For details, see the
finish.pyscript. The details are as follows:import os import argparse import subprocess parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Finish test_mobile_lenet.py case") parser.add_argument("--kill_tag", type=str, default="mindspore-lite-java-flclient") args, _ = parser.parse_known_args() kill_tag = args.kill_tag cmd = "pid=`ps -ef|grep " + kill_tag cmd += " |grep -v \"grep\" | grep -v \"finish\" |awk '{print $2}'` && " cmd += "for id in $pid; do kill -9 $id && echo \"killed $id\"; done" subprocess.call(['bash', '-c', cmd])
Run the following command to shut down the client:
python finish.py --kill_tag=mindspore-lite-java-flclient
The parameter
--kill_tagis used to search for the keyword to kill the client process. You only need to set the special keyword in--jarPath. The default value ismindspore-lite-java-flclient, that is, the name of the federated learning JAR package.The user can check whether the process still exists through the command
ps -ef |grep "mindspore-lite-java-flclient".**Experimental results of 50 clients participating in federated learning and training tasks. **
Currently, the
3500_clients_binfolder contains data of 3500 clients. This script can simulate a maximum of 3500 clients to participate in federated learning.The following figure shows the accuracy of the test dataset for federated learning on 50 clients (set
server_numto 16).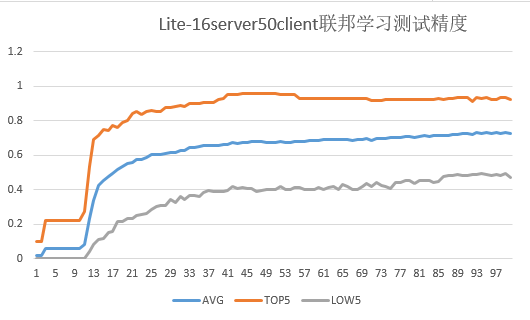
The total number of federated learning iterations is 100, the number of epochs for local training on the client is 20, and the value of batchSize is 32.
The test accuracy in the figure refers to the accuracy of each client test dataset on the aggregated model on the cloud for each federated learning iteration:
AVG: average accuracy of 50 client test datasets
TOP5: average accuracy of the five clients with the highest accuracy in the test dataset
LOW5: average accuracy of the five clients with the lowest accuracy in the test dataset3
