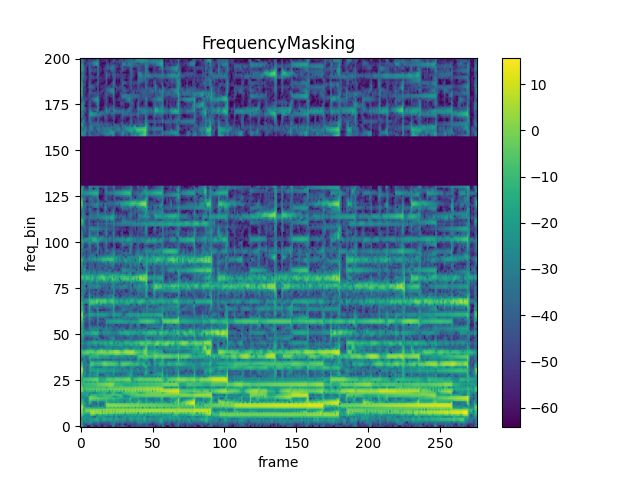
mindspore.dataset.audio.FrequencyMasking
- class mindspore.dataset.audio.FrequencyMasking(iid_masks=False, freq_mask_param=0, mask_start=0, mask_value=0.0)[source]
Apply masking to a spectrogram in the frequency domain.
Note
The shape of the audio waveform to be processed needs to be <…, freq, time>.
- Parameters
iid_masks (bool, optional) – Whether to apply different masks to each example/channel. Default:
False.freq_mask_param (int, optional) – When iid_masks is
True, length of the mask will be uniformly sampled from [0, freq_mask_param]; When iid_masks isFalse, directly use it as length of the mask. The value should be in range of [0, freq_length], where freq_length is the length of audio waveform in frequency domain. Default:0.mask_start (int, optional) – Starting point to apply mask, only works when iid_masks is
True. The value should be in range of [0, freq_length - freq_mask_param], where freq_length is the length of audio waveform in frequency domain. Default:0.mask_value (float, optional) – Value to assign to the masked columns. Default:
0.0.
- Raises
TypeError – If iid_masks is not of type bool.
TypeError – If freq_mask_param is not of type int.
ValueError – If freq_mask_param is greater than the length of audio waveform in frequency domain.
TypeError – If mask_start is not of type int.
ValueError – If mask_start is a negative number.
TypeError – If mask_value is not of type float.
ValueError – If mask_value is a negative number.
RuntimeError – If input tensor is not in shape of <…, freq, time>.
- Supported Platforms:
CPU
Examples
>>> import numpy as np >>> import mindspore.dataset as ds >>> import mindspore.dataset.audio as audio >>> >>> waveform = np.random.random([1, 3, 2]) >>> numpy_slices_dataset = ds.NumpySlicesDataset(data=waveform, column_names=["audio"]) >>> transforms = [audio.FrequencyMasking(freq_mask_param=1)] >>> numpy_slices_dataset = numpy_slices_dataset.map(operations=transforms, input_columns=["audio"])
- Tutorial Examples: