模型推理(C++接口)
MindSpore已经统一了端边云推理API,如您想继续使用MindSpore Lite独立API进行端侧推理,可以参考此文档。
概述
通过MindSpore Lite模型转换工具转换成.ms模型后,即可在Runtime中执行模型的推理流程。本教程介绍如何使用C++接口执行推理。
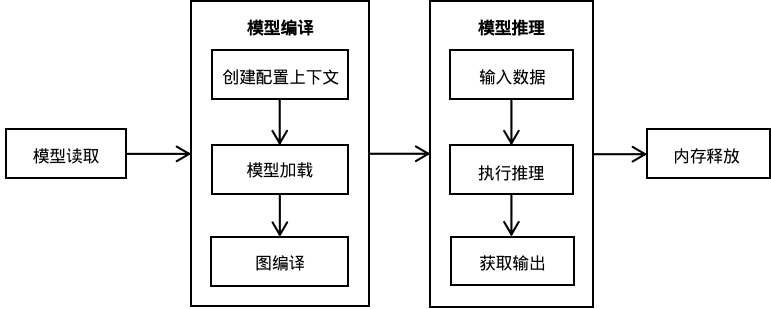
使用MindSpore Lite推理框架主要包括以下步骤:
模型读取:从文件系统中读取由模型转换工具转换得到的
.ms模型。创建配置上下文:创建配置上下文Context,保存需要的一些基本配置参数,用于指导模型编译和模型执行。
模型创建、加载与编译:执行推理之前,需要调用Model的Build接口进行模型加载和模型编译。模型加载阶段将文件缓存解析成运行时的模型。模型编译阶段主要进行算子选型调度、子图切分等过程,该阶段会耗费较多时间所以建议Model创建一次,编译一次,多次推理。
输入数据:模型执行之前需要向
输入Tensor中填充数据。获得输出:模型执行结束之后,可以通过
输出Tensor得到推理结果。释放内存:无需使用MindSpore Lite推理框架时,需要释放已创建的Model。
快速了解MindSpore Lite执行推理的完整调用流程,请参考体验MindSpore Lite C++极简Demo。
模型读取
通过MindSpore Lite进行模型推理时,需要从文件系统读取模型转换工具转换得到的.ms模型文件。
下面示例代码演示了从文件系统读取MindSpore Lite模型。
// Read model file.
size_t size = 0;
char *model_buf = ReadFile(model_path, &size);
if (model_buf == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "Read model file failed." << std::endl;
}
创建配置上下文
上下文会保存一些所需的基本配置参数,用于指导模型编译和模型执行,如果用户通过new创建Context,不再需要时,需要用户通过delete释放。一般在创建编译完Model后,Context即可释放。
MindSpore Lite默认执行的后端是CPU,Context创建后调用MutableDeviceInfo返回后端信息列表的引用,向列表中添加默认的CPUDeviceInfo。
下面示例代码演示了如何创建Context,配置默认的CPU后端,并设定CPU使能float16推理。
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
auto cpu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>();
if (cpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// CPU use float16 operator as priority.
cpu_device_info->SetEnableFP16(true);
device_list.push_back(cpu_device_info);
MutableDeviceInfo中支持用户设置设备信息,包括CPUDeviceInfo、GPUDeviceInfo、KirinNPUDeviceInfo、AscendDeviceInfo。设置的设备个数不能超过3个,推理过程按照用户设置的先后顺序选择后端设备进行部署推理。float16需要CPU为ARM v8.2架构的机型才能生效,其他不支持的机型和x86平台会自动回退到float32执行。
对于iOS设备,暂时只支持向
MutableDeviceInfo添加CPU后端,且暂时不支持CPU后端float16的执行。
Context中包含的配置API如下:
配置线程数
Context通过SetThreadNum配置线程数:
// Configure the number of worker threads in the thread pool to 2, including the main thread.
context->SetThreadNum(2);
配置线程亲和性
Context通过SetThreadAffinity配置线程和CPU绑定。如果参数是int mode,配置绑核策略,有效值为0-2,0为默认不绑核,1为优先绑大核,2为优先绑小核。如果参数是const std::vector<int> &core_list,配置绑核列表。同时配置时,core_list生效,mode不生效。
// Configure the thread to be bound to the big core first.
// Valid value: 0: no affinities, 1: big cores first, 2: little cores first
context->SetThreadAffinity(1);
配置并行策略
Context通过SetEnableParallel配置执行推理时是否支持并行。
// Configure the inference supports parallel.
context->SetEnableParallel(true);
配置使用GPU后端
当需要执行的后端为GPU时,需要设置GPUDeviceInfo为首选推理后端。建议设置CPUDeviceInfo为次选后端,排在GPU后,以保证泛化模型的推理。其中GPUDeviceInfo通过SetEnableFP16使能float16推理。
下面示例代码演示如何创建CPU与GPU异构推理后端,同时GPU也设定使能float16推理:
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
// Set GPU device first, make GPU preferred backend.
auto gpu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::GPUDeviceInfo>();
if (gpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New GPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// GPU use float16 operator as priority.
gpu_device_info->SetEnableFP16(true);
// Set VNIDIA device id, only valid when GPU backend is TensorRT.
gpu_device_info->SetDeviceID(0);
// The GPU device context needs to be push_back into device_list to work.
device_list.push_back(gpu_device_info);
// Set CPU device after GPU as second choice.
auto cpu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>();
if (cpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// CPU use float16 operator as priority.
cpu_device_info->SetEnableFP16(true);
device_list.push_back(cpu_device_info);
目前GPU的后端,区分
arm64和x86_64平台。
在
arm64上是基于OpenCL,支持Mali、Adreno的GPU,OpenCL版本为2.0。具体配置为:
CL_TARGET_OPENCL_VERSION=200
CL_HPP_TARGET_OPENCL_VERSION=120
CL_HPP_MINIMUM_OPENCL_VERSION=120
在
x86_64上是基于TensorRT的GPU,TensorRT版本为6.0.1.5。
SetEnableFP16属性是否设置成功取决于当前设备的CUDA计算能力。SetDeviceID属性仅在TensorRT的GPU上有效,用于指定NVIDIA显卡。
配置使用NPU后端
当需要执行的后端为NPU时,需要设置KirinNPUDeviceInfo为首选推理后端。建议设置CPUDeviceInfo为次选后端,排在NPU后,以保证泛化模型的推理。其中KirinNPUDeviceInfo通过SetFrequency来设置NPU频率。
下面示例代码如何创建CPU与NPU异构推理后端,同时NPU频率设置为3。频率值默认为3,可设置为1(低功耗)、2(均衡)、3(高性能)、4(极致性能):
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
// Set NPU device first, make NPU preferred backend.
auto npu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::KirinNPUDeviceInfo>();
if (npu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New KirinNPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// NPU set frequency to be 3.
npu_device_info->SetFrequency(3);
// The NPU device context needs to be push_back into device_list to work.
device_list.push_back(npu_device_info);
// Set CPU device after NPU as second choice.
auto cpu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>();
if (cpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// CPU use float16 operator as priority.
cpu_device_info->SetEnableFP16(true);
device_list.push_back(cpu_device_info);
配置使用NNIE后端
当需要执行的后端为CPU和NNIE的异构推理时,只需要按照配置使用CPU后端的方法创建好Context即可,无需指定provider。
配置使用Ascend后端
当需要执行的后端为Ascend时(目前支持Atlas 200/300/500推理产品),需要设置AscendDeviceInfo为首选推理后端。建议设置CPUDeviceInfo为次选后端,排在Ascend后,以保证泛化模型的推理。其中Ascend310DeviceInfo通过SetDeviceID来设置设备ID。
下面[示例代码]如何创建CPU与Ascend异构推理后端,同时设备ID设置为0:
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
// Set Atlas 200/300/500 inference product device first, make Atlas 200/300/500 inference product preferred backend.
auto ascend_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::AscendDeviceInfo>();
if (ascend_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New AscendDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// Atlas 200/300/500 inference product set device id to be 0.
ascend_device_info->SetDeviceID(0);
// The Atlas 200/300/500 inference product device context needs to be push_back into device_list to work.
device_list.push_back(ascend_device_info);
// Set CPU device after Atlas 200/300/500 inference product as second choice.
auto cpu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>();
if (cpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
device_list.push_back(cpu_device_info);
配置使用CoreML后端
当需要执行的后端为CoreML时,只需实例化CoreMLDelegate类,并将实例对象通过SetDelegate接口传入上下文对象(context)即可。这与NPU和GPU等以硬件为区分的后端配置步骤有些许不同。
下面示例代码演示了如何创建CPU与CoreML异构推理后端:
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
// Set CPU device after NPU as second choice.
auto cpu_device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>();
if (cpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
device_list.push_back(cpu_device_info);
auto coreml_delegate = std::make_shared<CoreMLDelegate>();
if (coreml_delegate == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New CoreMLDelegate failed." << std::endl;
}
context->SetDelegate(coreml_delegate);
当前CoreML后端暂时只支持操作系统版本不低于iOS 11的设备。
模型创建加载与编译
使用MindSpore Lite执行推理时,Model是推理的主入口,通过Model可以实现模型加载、模型编译和模型执行。采用上一步创建得到的Context,调用Model的复合Build接口来实现模型加载与模型编译。
下面示例代码演示了Model创建、加载与编译的过程:
// Create model
auto model = new (std::nothrow) mindspore::Model();
if (model == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New Model failed." << std::endl;
}
// Build model
auto build_ret = model->Build(model_buf, size, mindspore::kMindIR, context);
delete[](model_buf);
// After the model is built, the Context can be released.
...
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Build model failed." << std::endl;
}
创建并编译完Model后,上一步创建得到的Context即可释放。
针对大模型,使用model buffer进行加载编译的时候需要单独设置权重文件的路径,通过LoadConfig或UpdateConfig接口设置模型路径,其中
section为model_file,key为mindir_path;使用model path进行加载编译的时候不需要设置其他参数,会自动读取权重参数。用户在源码编译时如果启用了
MSLITE_ENABLE_MODEL_PRE_INFERENCE功能,运行时会在Build阶段(非加密场景)默认进行预推理,以检测程序是否能正常执行。该功能可通过LoadConfig或UpdateConfig接口设置关闭,其中section为common,key为enable_pre_inference,value为true或false。
输入数据
在模型执行前,需要获取到模型的输入MSTensor,将输入数据通过memcpy拷贝到模型的输入Tensor。可以通过MSTensor的DataSize方法来获取Tensor应该填入的数据大小,通过DataType方法来获取Tensor的数据类型,通过MutableData方法来获取可写的指针。
MindSpore Lite提供两种方法来获取模型的输入Tensor。
使用GetInputByTensorName方法,根据Tensor的名称来获取模型输入Tensor,下面示例代码演示如何调用
GetInputByTensorName获得输入Tensor并填充数据。// Pre-processing of input data, convert input data format to NHWC. ... // Assume that the model has only one input tensor named graph_input-173. auto in_tensor = model->GetInputByTensorName("graph_input-173"); if (in_tensor == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Input tensor is nullptr" << std::endl; } auto input_data = in_tensor.MutableData(); if (input_data == nullptr) { std::cerr << "MallocData for inTensor failed." << std::endl; } memcpy(in_data, input_buf, data_size); // Users need to free input_buf.
使用GetInputs方法,直接获取所有的模型输入Tensor的vector,下面示例代码演示如何调用
GetInputs获得输入Tensor并填充数据。// Pre-processing of input data, convert input data format to NHWC. ... // Assume we have created a Model instance named model. auto inputs = model->GetInputs(); // Assume that the model has only one input tensor. auto in_tensor = inputs.front(); if (in_tensor == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Input tensor is nullptr" << std::endl; } auto *in_data = in_tensor.MutableData(); if (in_data == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Data of in_tensor is nullptr" << std::endl; } memcpy(in_data, input_buf, data_size); // Users need to free input_buf.
MindSpore Lite的模型输入Tensor中的数据排布必须是
NHWC。如果需要了解更多数据前处理过程,可参考基于JNI接口的Android应用开发中编写端侧推理代码的第2步,将输入图片转换为传入MindSpore模型的Tensor格式。GetInputs和GetInputByTensorName方法返回的数据不需要用户释放。
执行推理
MindSpore Lite调用Model的Predict进行模型推理。
下面示例代码演示调用Predict执行推理。
auto inputs = model->GetInputs();
auto outputs = model->GetOutputs();
auto predict_ret = model->Predict(inputs, &outputs);
if (predict_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Predict error " << predict_ret << std::endl;
}
获取输出
MindSpore Lite在执行完推理后,就可以获取模型的推理结果。MindSpore Lite提供三种方法来获取模型的输出MSTensor。
使用GetOutputsByNodeName方法,根据模型输出节点的名称来获取模型输出Tensor中连接到该节点的Tensor的vector,下面示例代码演示如何调用
GetOutputsByNodeName获得输出Tensor。// Assume we have created a Model instance named model before. // Assume that model has a output node named Softmax-65. auto output_vec = model->GetOutputsByNodeName("Softmax-65"); // Assume that output node named Default/Sigmoid-op204 has only one output tensor. auto out_tensor = output_vec.front(); if (out_tensor == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Output tensor is nullptr" << std::endl; } // Post-processing your result data.
使用GetOutputByTensorName方法,根据模型输出Tensor的名称来获取对应的模型输出Tensor,下面示例代码演示如何调用
GetOutputByTensorName获得输出Tensor。// Assume we have created a Model instance named model. // We can use GetOutputTensorNames method to get all name of output tensor of model which is in order. auto tensor_names = model->GetOutputTensorNames(); // Assume we have created a Model instance named model before. for (auto tensor_name : tensor_names) { auto out_tensor = model->GetOutputByTensorName(tensor_name); if (out_tensor == nullptr) { std::cerr << "Output tensor is nullptr" << std::endl; } // Post-processing the result data. }
使用GetOutputs方法,直接获取所有的模型输出Tensor的vector,下面示例代码演示如何调用
GetOutputs获得输出Tensor。// Assume we have created a Model instance named model. auto out_tensors = model->GetOutputs(); for (auto out_tensor : out_tensors) { // Post-processing the result data. }
GetOutputsByNodeName、GetOutputByTensorName和GetOutputs方法返回的数据不需要用户释放。
内存释放
无需使用MindSpore Lite推理框架时,需要释放已经创建的Model,下列示例代码演示如何在程序结束前进行内存释放。
// Delete model.
// Assume that the variable of Model * is named model.
delete model;
高级用法
输入维度Resize
使用MindSpore Lite进行推理时,如果需要对输入的shape进行Resize,则可以在已完成创建Model与模型编译Build之后调用Model的Resize接口,对输入的Tensor重新设置shape。
某些网络是不支持可变维度,会提示错误信息后异常退出,比如,模型中有MatMul算子,并且MatMul的一个输入Tensor是权重,另一个输入Tensor是输入时,调用可变维度接口会导致输入Tensor和权重Tensor的Shape不匹配,最终导致推理失败。
TensorRT的GPU后端只支持在NHWC输入格式下的NHW维度的resize,且resize维度的shape值,不能大于创建的Model的输入shape值。
下面示例代码演示如何对MindSpore Lite的输入Tensor进行Resize:
// Assume we have created a Model instance named model.
auto inputs = model->GetInputs();
std::vector<int64_t> resize_shape = {1, 128, 128, 3};
// Assume the model has only one input,resize input shape to [1, 128, 128, 3]
std::vector<std::vector<int64_t>> new_shapes;
new_shapes.push_back(resize_shape);
return model->Resize(inputs, new_shapes);
混合精度运行
MindSpore Lite 支持混合精度推理。 用户可以在完成创建Model之后,在模型编译Build之前,调用Model的LoadConfig接口,配置混合精度信息。 配置文件举例,内容如下:
[execution_plan]
op_name1=data_type:float16
op_name2=data_type:float32
下面示例代码演示如何进行混合精度推理:
Status load_config_ret = model->LoadConfig(config_file_path);
if (load_config_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Model load config error " << load_config_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
Status build_ret = model->Build(graph_cell, context);
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Model build error " << build_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
auto inputs = model->GetInputs();
auto outputs = model->GetOutputs();
Status predict_ret = model->Predict(inputs, &outputs);
if (predict_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Model predict error " << predict_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
多硬件异构运行
MindSpore Lite 支持多硬件异构推理。 用户可以在Context中配置多个DeviceInfoContext,并且根据设备的先后顺序,设置异构硬件的运行优先级。
下面示例代码演示如何进行多硬件异构推理:
mindspore::Context context;
// enable NPU CPU GPU in inference. NPU is preferentially used, then the CPU, and GPU get the lowest priority.
context.MutableDeviceInfo().push_back(std::make_shared<mindspore::KirinNPUDeviceInfo>());
context.MutableDeviceInfo().push_back(std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>());
context.MutableDeviceInfo().push_back(std::make_shared<mindspore::GPUDeviceInfo>());
Status build_ret = model->Build(graph_cell, context);
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Model build error " << build_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
auto inputs = model->GetInputs();
auto outputs = model->GetOutputs();
Status predict_ret = model->Predict(inputs, &outputs);
if (predict_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Model predict error " << predict_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
OpenGL纹理输入
MindSpore Lite 支持 OpenGL纹理输入,进行端到端的GPU同构推理,推理结果以OpenGL纹理数据返回。该功能在使用过程中需要配置到Context中,和在运行推理时绑定OpenGL纹理数据,这两个过程。
配置 Context
用户需要将 Context 中的 devgpu_device_info_中的 SetEnableGLTexture 属性设置为 true,并且将用户当前的OpenGL EGLContext、EGLDisplay分别通过SetGLContext接口和SetGLDisplay接口进行配置。
const std::shared_ptr<mindspore::Context> context; auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo(); // 1. Set EnableGLTexture true gpu_device_info->SetEnableGLTexture(true); // 2. Set GLContext auto gl_context = eglGetCurrentContext(); gpu_device_info->SetGLContext(gl_context); // 3. Set GLDisplay auto gl_display = eglGetCurrentDisplay(); gpu_device_info->SetGLDisplay(gl_display);
绑定OpenGL纹理数据
在模型编译阶段后,模型运行前,用户需要调用 BindGLTexture2DMemory(const std::map<std::string, GLuint> &inputGlTexture, std::map<std::string, GLuint> *outputGLTexture;) 函数绑定输入输出纹理,代替原有输入数据的步骤,因为 MindSpore Lite 本身并没有分配 OpenGL 内存的功能,所以要求用户根据模型输入输出的 tensor size 事先创建好输入输出纹理的内存,并将纹理内存对应的纹理 ID 绑定到模型的输入输出,示例代码如下
std::map<std::string, GLuint> input_gl_texture; std::map<std::string, GLuint> output_gl_texture; ... // Write OpenGL Texture data(GLuint) into input_gl_texture and output_gl_texture // Bind texture data with input and output tensors auto status = ms_model_.BindGLTexture2DMemory(input_gl_texture, &output_gl_texture); if (status != kSuccess) { MS_LOG(ERROR) << "BindGLTexture2DMemory failed"; return kLiteError; } return kSuccess;
std::map<std::string, GLuint> input_gl_texture 变量中key为模型输入tensor name,value为对应的GLuint 纹理;std::map<std::string, GLuint> output_gl_texture 变量中key为模型输出tensor name,value为对应的GLuint 纹理。模型输入输出tensor name可以通过tensor.Name()接口获取,示例代码如下:
std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> inputs; vector<GLuint> inTextureIDs; for (auto i; i < inputs.size(); i++) { inputGlTexture.insert(std::pair<std::string, GLuint>(inputs.at(i).Name(), inTextureIDs.at(i)); } std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> outputs; vector<GLuint> outTextureIDs; for (auto i; i < inputs.size(); i++) { outputGlTexture.insert(std::pair<std::string, GLuint>(inputs.at(i).Name(), outTextureIDs.at(i)); }
Predict结果
绑定完成后直接调用ms_model_的 Predict 接口进行推理即可,模型输出会被拷贝到绑定的输出纹理 ID 对应的内存上,用户可从outputs上面获取推理结果
std::vector<MSTensor> outputs; auto ret = ms_model_.Predict(ms_inputs_for_api_, &outputs, ms_before_call_back_, ms_after_call_back_); if (ret != kSuccess) { MS_LOG(ERROR) << "Inference error "; std::cerr << "Inference error " << std::endl; return kLiteError; }
共享内存池
如果存在多个Model的情况,可以通过在DeviceInfoContext中配置同一个Allocator,实现共享内存池来减少运行时内存大小。其中,内存池的内存总大小限制为3G,单次分配的内存限制为2G。
下面示例代码演示如何在两个Model间共享内存池的功能:
auto context1 = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context1 == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list1 = context1->MutableDeviceInfo();
auto device_info1 = CreateCPUDeviceInfo();
if (device_info1 == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "Create CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
device_list1.push_back(device_info1);
auto model1 = new (std::nothrow) mindspore::Model();
if (model1 == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New Model failed." << std::endl;
}
auto build_ret = model1->Build(model_buf, size, mindspore::kMindIR, context1);
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Build model failed." << std::endl;
}
auto context2 = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context2 == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list2 = context2->MutableDeviceInfo();
auto device_info2 = CreateCPUDeviceInfo();
if (device_info2 == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "Create CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
// Use the same allocator to share the memory pool.
device_info2->SetAllocator(device_info1->GetAllocator());
device_list2.push_back(device_info2);
auto model2 = new (std::nothrow) mindspore::Model();
if (model2 == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New Model failed." << std::endl;
}
build_ret = model2->Build(model_buf, size, mindspore::kMindIR, context2);
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Build model failed." << std::endl;
}
回调运行
MindSpore Lite可以在调用Predict时,传入两个MSKernelCallBack函数指针来回调推理模型,相比于一般的模型执行,回调运行可以在运行过程中获取额外的信息,帮助开发者进行性能分析、Bug调试等。额外的信息包括:
当前运行的节点名称
推理当前节点前的输入输出Tensor
推理当前节点后的输入输出Tensor
下面示例代码演示如何定义了两个回调函数作为前置回调指针和后置回调指针,传入到Predict接口进行回调推理。
// Definition of callback function before forwarding operator.
auto before_call_back = [](const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &before_inputs,
const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &before_outputs,
const mindspore::MSCallBackParam &call_param) {
std::cout << "Before forwarding " << call_param.node_name_ << " " << call_param.node_type_ << std::endl;
return true;
};
// Definition of callback function after forwarding operator.
auto after_call_back = [](const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &after_inputs,
const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &after_outputs,
const mindspore::MSCallBackParam &call_param) {
std::cout << "After forwarding " << call_param.node_name_ << " " << call_param.node_type_ << std::endl;
return true;
};
auto inputs = model->GetInputs();
auto outputs = model->GetOutputs();
auto predict_ret = model->Predict(inputs, &outputs, before_call_back, after_call_back);
if (predict_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Predict error " << predict_ret << std::endl;
}
模型加载与编译独立调用流程
模型加载与编译也可以分别调用Serialization的Load接口和Model的Build实现。
下面示例代码演示模型加载与编译独立调用的流程:
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
if (context == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New context failed." << std::endl;
}
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
auto cpu_device_info = CreateCPUDeviceInfo();
if (cpu_device_info == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "Create CPUDeviceInfo failed." << std::endl;
}
device_list.push_back(cpu_device_info);
// Load graph
mindspore::Graph graph;
auto load_ret = mindspore::Serialization::Load(model_buf, size, mindspore::kMindIR, &graph);
if (load_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Load graph failed." << std::endl;
}
// Create model
auto model = new (std::nothrow) mindspore::Model();
if (model == nullptr) {
std::cerr << "New Model failed." << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
// Build model
mindspore::GraphCell graph_cell(graph);
auto build_ret = model->Build(graph_cell, context);
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
std::cerr << "Build model failed." << std::endl;
}
模型解密推理
当模型被converter_lite工具转换时加密,在lite加载模型时需通过传入密钥和解密工具相关参数。其中,dec_key应与使用converter_lite工具加密时的密钥一致,均十六进制表示的字符串。如b'0123456789ABCDEF'对应的十六进制表示为30313233343536373839414243444546,Linux平台用户可以使用xxd工具对字节表示的密钥进行十六进制表达转换。crypto_lib_path为该环境中openssl的安装路径,如"/home/root/openssl"。
下面示例代码演示模型解密加载及推理的流程:
int RunEncryptedInfer(const char *model_path, const std::string dec_key_str,
const std::string crypto_lib_path) {
// Set Context
auto context = std::make_shared<mindspore::Context>();
auto &device_list = context->MutableDeviceInfo();
auto device_info = std::make_shared<mindspore::CPUDeviceInfo>();
device_list.push_back(device_info);
// Create model
auto model = new (std::nothrow) mindspore::Model();
// Set Decrypt Parameters
mindspore::Key dec_key;
std::string dec_mode = "AES-GCM";
dec_key.len = Hex2ByteArray(dec_key_str, dec_key.key, kEncMaxLen);
// Build model
auto build_ret = model->Build(model_path, mindspore::kMindIR, context, dec_key, dec_mode, crypto_lib_path);
if (build_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
delete model;
std::cerr << "Build model error " << build_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Predict
auto inputs = model->GetInputs();
auto outputs = model->GetOutputs();
auto predict_ret = model->Predict(inputs, &outputs);
if (predict_ret != mindspore::kSuccess) {
delete model;
std::cerr << "Predict error " << predict_ret << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Delete model.
delete model;
return 0;
如使用converter_lite工具的命令为:
./converter_lite --fmk=MINDIR --modelFile=./lenet.mindir --outputFile=lenet_enc --encryptKey=30313233343536373839414243444546 --encryption=true
在mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_cpp目录下编译源码生成build/runtime_cpp文件:
cd mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_cpp
bash build.sh
cd build
运行Lite端侧使用加密后的模型进行推理:
./runtime_cpp --modelFile=./lenet_enc.ms 6 30313233343536373839414243444546 ${your_openssl_path}
查看日志
当推理出现异常的时候,可以通过查看日志信息来定位问题。针对Android平台,采用Logcat命令行工具查看MindSpore Lite推理的日志信息,并利用MS_LITE 进行筛选。
logcat -s "MS_LITE"
对iOS设备暂不支持日志查看。
获取版本号
MindSpore Lite提供了Version方法可以获取版本号,包含在include/api/types.h头文件中,调用该方法可以得到当前MindSpore Lite的版本号。
下面示例代码演示如何获取MindSpore Lite的版本号:
#include "include/api/types.h"
std::string version = mindspore::Version();
扩展使用
本章节提供了扩展MindSpore Lite推理框架的示例程序,通过演示自定义算子的构建、注册的全流程,用户能够快速了解推理框架的扩展API的使用,能够在推理框架中集成自定义算子。本章节以一个具有简易Add计算能力的Custom单算子为模型。相关代码放置在mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend目录。
本章节仅提供了在Linux环境下的使用说明。
算子InferShape扩展
用户需继承KernelInterface类,重载Infer接口函数。
Status CheckInputs(const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &inputs) { // 输入校验函数,校验输入张量的shape是否合规
for (auto &input : inputs) {
auto input_shape = input.Shape();
if (std::find(input_shape.begin(), input_shape.end(), -1) != input_shape.end()) {
return kLiteInferInvalid;
}
}
return kSuccess;
}
class CustomAddInfer : public kernel::KernelInterface {
public:
CustomAddInfer() = default;
~CustomAddInfer() = default;
Status Infer(std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> *inputs, std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> *outputs,
const schema::Primitive *primitive) override { // 重载Infer公有函数
(*outputs)[0].SetFormat((*inputs)[0].format());
(*outputs)[0].SetDataType((*inputs)[0].DataType());
auto ret = CheckInputs(inputs);
if (ret == kLiteInferInvalid) {
(*outputs)[0].SetShape({-1}); // 输出张量的shape设为{-1},表示在运行时需要再次推断
return kLiteInferInvalid;
} else if (ret != kSuccess) {
return kLiteError;
}
(*outputs)[0].SetShape((*inputs)[0].Shape());
return kSuccess;
}
};
std::shared_ptr<kernel::KernelInterface> CustomAddInferCreator() { return std::make_shared<CustomAddInfer>(); }
REGISTER_CUSTOM_KERNEL_INTERFACE(CustomOpTutorial, Custom_Add, CustomAddInferCreator) // 调用注册接口
shape推断分为两个时期,一是图编译时的静态推断,二是图运行时的动态推断。
静态推断:
CheckInputs失败或者当前节点需要动态推断的情形下,需将输出张量的shape设为{-1},以便在图运行时的识别标识,且返回码需设置为kLiteInferInvalid。其他情形下,返回其他错误码,程序将会停止,请进行必要的检查。
动态推断:
在算子运行时,动态推断是否需要,依据对输出张量的shape校验。请参考下面的算子扩展说明。
算子扩展
用户需继承Kernel类,重载必要的接口。
Prepare:此接口将在图编译期间调用,用户可对算子做运行前的准备或者必要的校验。
Execute:此接口是算子的运行接口,用户可将动态推断逻辑PreProcess放置于此接口内调用。
Status CheckOutputs(const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &outputs) { // 算子运行时校验,以确定是否调用InferShape过程 for (auto &output : outputs) { auto output_shape = output.Shape(); if (std::find(output_shape.begin(), output_shape.end(), -1) != output_shape.end()) { return kLiteInferInvalid; } } return kSuccess; }
ReSize:此接口用于在图输入shape变化的情形下,当前算子所需的相应变动。
属性解析:用户需自行提供对算子属性的解析,可参考ParseAttrData。
算子注册,API接口可参考REGISTER_CUSTOM_KERNEL。
const auto kFloat32 = DataType::kNumberTypeFloat32; std::shared_ptr<Kernel> CustomAddCreator(const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &inputs, const std::vector<mindspore::MSTensor> &outputs, const schema::Primitive *primitive, const mindspore::Context *ctx) { return std::make_shared<CustomAddKernel>(inputs, outputs, primitive, ctx); } REGISTER_CUSTOM_KERNEL(CPU, CustomOpTutorial, kFloat32, Custom_Add, CustomAddCreator)
示例演示
编译
环境要求
编译构建
在
mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend目录下执行build.sh,将自动下载MindSpore Lite发布件并编译Demo。bash build.sh若使用该build脚本下载MindSpore Lite发布件失败,请手动下载硬件平台为CPU、操作系统为Ubuntu-x64的MindSpore Lite发布件mindspore-lite-{version}-linux-x64.tar.gz,将解压后
runtime/lib目录下的libmindspore-lite.so文件拷贝到mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend/lib目录、runtime/include目录拷贝到mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend目录下。若
add_extend.ms模型下载失败,请手动下载相关模型文件add_extend.ms,并将其拷贝到mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend/model目录。通过手动下载并且将该文件放到指定位置后,需要再次执行build.sh脚本才能完成编译构建。
编译输出
在
mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend/build目录下生成了runtime_extend_tutorial的可执行程序。
执行程序
编译构建后,进入
mindspore/lite/examples/runtime_extend/build目录,并执行以下命令,体验扩展的MindSpore Lite推理add_extend.ms模型。./runtime_extend_tutorial ../model/add_extend.ms执行完成后将能得到如下结果,打印输出Tensor的名称、输出Tensor的大小,输出Tensor的数量以及前20个数据:
tensor name is:add-0 tensor size is:400 tensor elements num is:100 output data is:2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2