Using Java Interface to Perform Cloud-side Inference
Overview
After converting the .mindir model by MindSpore Lite model conversion tool, you can execute the inference process of the model in Runtime. This tutorial describes how to perform cloud-side inference by using the JAVA interface.
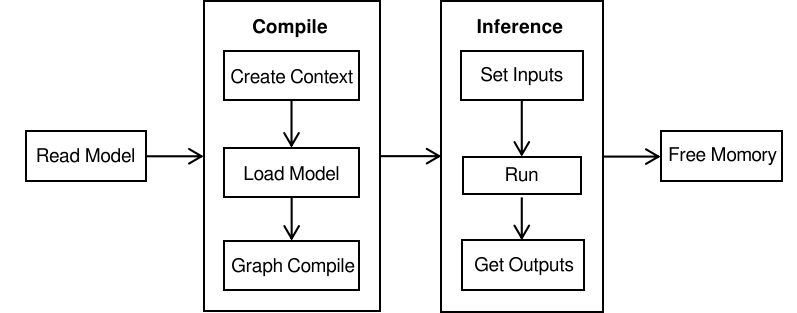
Compared with C++ API, Java API can be called directly in Java Class, and users do not need to implement the code related to JNI layer, with better convenience. Running MindSpore Lite inference framework mainly consists of the following steps:
Model reading: Export MindIR model via MindSpore or get MindIR model by model conversion tool.
Create configuration context: Create a configuration context MSContext and save some basic configuration parameters used to guide model compilation and model execution, including device type, number of threads, CPU pinning, and enabling fp16 mixed precision inference.
Model creation, loading and compilation: Before executing inference, you need to call build interface of Model for model loading and model compilation. Both loading files and MappedByteBuffer are currently supported. The model loading phase parses the file or buffer into a runtime model.
Input data: The model needs to be padded with data from the input Tensor before execution.
Execute inference: Use predict of Model method for model inference.
Obtain the output: After the graph execution, the inference result can be obtained by outputting the Tensor.
Release memory: When there is no need to use MindSpore Lite inference framework, you need to release the created Model.
Reference to MindSpore Lite Java Library
Linux Project References to JAR Library
When using Maven as a build tool, you can copy mindspore-lite-java.jar to the lib directory in the root directory and add the jar package dependencies in pom.xml.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mindspore.lite</groupId>
<artifactId>mindspore-lite-java</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>${project.basedir}/lib/mindspore-lite-java.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Model Path
To perform model inference with MindSpore Lite, you need to get the path of the .mindir model file in the file system converted by Model Conversion Tool.
Creating Configuration Context
Create a configuration context MSContext and save some basic configuration parameters required for the session, which is used to guide graph compilation and graph execution. Configure the number of threads, thread affinity and whether to enable heterogeneous parallel inference via the init interface. MindSpore Lite has a built-in thread pool shared by processes. The maximum number of threads in the pool is specified by threadNum when inference, and the default is 2 threads.
The backend of MindSpore Lite inference can call deviceType in the AddDeviceInfo interface to specify, currently supporting CPU, GPU and Ascend. When graph compilation is performed, the operator selection is scheduled based on the main selection backend. If the backend supports float16, float16 operator can be used in preference by setting isEnableFloat16 to true.
Configuring to Use the CPU Backend
When the backend to be executed is CPU, MSContext needs to be initialized in DeviceType.DT_CPU of addDeviceInfo, while the CPU supports setting the CPU pinning mode and whether to use float16 operator in preference.
The following demonstrates how to create a CPU backend, set the number of threads to 2, set the CPU pinning mode to large core priority and enable float16 inference, and turn off parallelism:
MSContext context = new MSContext();
context.init(2, CpuBindMode.HIGHER_CPU);
context.addDeviceInfo(DeviceType.DT_CPU, true);
Configuring to Use the GPU Backend
When the backend to be executed is GPU, after MSContext is created, you need to add GPUDeviceInfo in the addDeviceInfo. If float16 inference is enabled, the GPU will use the float16 operator in preference.
The following code demonstrates how to create a GPU inference backend:
MSContext context = new MSContext();
context.init();
context.addDeviceInfo(DeviceType.DT_GPU, true);
Configuring to Use the Ascend Backend
When the backend to be executed is Ascend, MSContext needs to be initialized DeviceType.DT_ASCEND in addDeviceInfo.
The following demonstrates how to create an Ascend backend:
MSContext context = new MSContext();
context.init();
context.addDeviceInfo(DeviceType.DT_ASCEND, false, 0);
Model Creation, Loading and Compilation
When using MindSpore Lite to perform inference, Model is the main entry for inference. Model loading, compilation and execution are implemented through Model. Using the MSContext created in the previous step, call the compound build interface of Model to implement model loading and model compilation.
The following demonstrates the process of Model creation, loading and compilation:
Model model = new Model();
boolean ret = model.build(filePath, ModelType.MT_MINDIR, msContext);
Inputting the Data
MindSpore Lite Java interface provides getInputsByTensorName and getInputs methods to get the input Tensor, and supports byte[] or ByteBuffer types of data, set the input Tensor data by setData.
Use getInputsByTensorName method. Obtain the Tensor connected to the input node in the model input Tensor based on the name of the model input Tensor. The following demonstrates how to call
getInputsByTensorNameto get the input Tensor and pad the data.MSTensor inputTensor = model.getInputsByTensorName("2031_2030_1_construct_wrapper:x"); // Set Input Data. inputTensor.setData(inputData);
Use getInputs method and obtain all the model input Tensor vectors directly. The following demonstrates how to call
getInputsto get the input Tensor and pad the data.List<MSTensor> inputs = model.getInputs(); MSTensor inputTensor = inputs.get(0); // Set Input Data. inputTensor.setData(inputData);
Executing the Inference
MindSpore Lite can call predict of Model to execute model inference after the model is compiled.
The following sample code demonstrates calling predict to perform inference.
// Run graph to infer results.
boolean ret = model.predict();
Obtaining the Output
MindSpore Lite can get the inference result by outputting Tensor after performing inference. MindSpore Lite provides three methods to get the output of the model MSTensor, and also supports getByteData, getFloatData, getIntData, getLongData four methods to get the output data.
Use the getOutputs method, get all the model to output list of MSTensor. The following demonstrates how to call
getOutputsto get the list of output Tensor.List<MSTensor> outTensors = model.getOutputs();
Use the getOutputsByNodeName method and get the vector of the Tensor connected to that node in the model output MSTensor according to the name of model output node. The following demonstrates how to call
getOutputByTensorNameto get the output Tensor.MSTensor outTensor = model.getOutputsByNodeName("Default/head-MobileNetV2Head/Softmax-op204"); // Apply infer results. ...
Use the getOutputByTensorName method to get the corresponding model output MSTensor based on the name of the model output Tensor. The following demonstrates how to call
getOutputByTensorNameto get the output Tensor.MSTensor outTensor = model.getOutputByTensorName("Default/head-MobileNetV2Head/Softmax-op204"); // Apply infer results. ...
Releasing the Memory
When there is no need to use the MindSpore Lite inference framework, it is necessary to free the created models. The following demonstrates how to do the memory release before the end of the program.
model.free();
Advanced Usage
Input Dimension Resize
When using MindSpore Lite for inference, if you need to Resize the input shape, you can call theResize of Model to reset the shape of the input Tensor after the model compiles build.
Some networks do not support variable dimensions and will exit abnormally after prompting an error message. For example, when there is a MatMul operator in the model and one input Tensor of MatMul is the weight and the other input Tensor is the input, calling the variable dimension interface will cause the Shape of the input Tensor and the weight Tensor to mismatch, which eventually fails the inference.
The following demonstrates how to Resize the input Tensor of MindSpore Lite:
List<MSTensor> inputs = model.getInputs();
int[][] dims = {{1, 300, 300, 3}};
bool ret = model.resize(inputs, dims);
Viewing the Logs
When an exception occurs in inference, the problem can be located by viewing log information.
Obtaining the Version Number
MindSpore Lite provides the Version method to get the version number, which is included in the com.mindspore.lite.config.Version header file. This method is called to get the current version number of MindSpore Lite.
The following demonstrates how to get the version number of MindSpore Lite:
import com.mindspore.lite.config.Version;
String version = Version.version();