Using Python Interface to Perform Concurrent Inference
Overview
MindSpore Lite provides a multi-model concurrent inference interface ModelParallelRunner, multi-model concurrent inference now supports Atlas 200/300/500 inference product, Atlas inference series (with Ascend 310P AI processor), Atlas training series, Nvidia GPU, CPU backends.
After exporting the mindir model by MindSpore or converting it by model conversion tool to obtain the mindir model, the concurrent inference process of the model can be executed in Runtime. This tutorial describes how to use the Python interface to perform concurrent inference with multiple models.
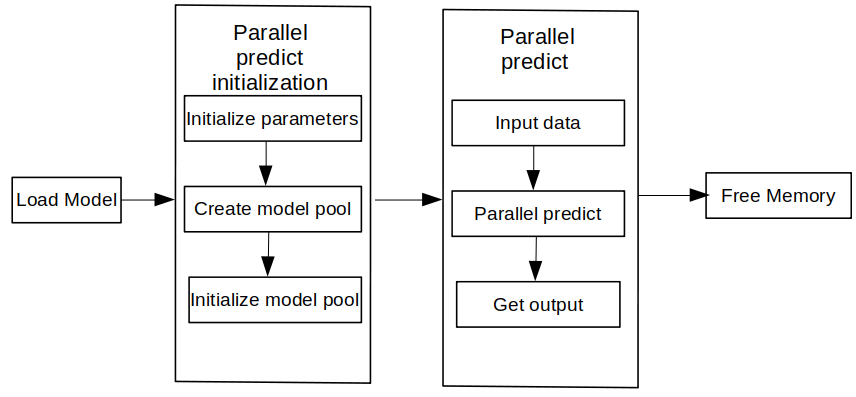
Concurrent inference with MindSpore Lite consists of the following main steps:
Preparation: Install the MindSpore Lite cloud-side inference Python package.
Create configuration context: Create a Context.parallel attributes to configure multi-model concurrency.
ModelParallelRunner creation and compilation: Before multi-model concurrent inference, you need to call build_from_file interface of ModelParallelRunner for ModelParallelRunner loading and compilation.
Setting Concurrent Inference Tasks: Create multiple threads and bind concurrent inference tasks.
Perform concurrent inference: Use Predict interface of ModelParallelRunner for multi-model concurrent inference.
Free memory: when there is no need to use the MindSpore Lite concurrent inference framework, you need to release the ModelParallelRunner you created and the associated Tensor.
Preparation
The following code samples are from Using Python interface to perform cloud-side inference sample code.
Export the MindIR model via MindSpore, or get the MindIR model by converting it with model conversion tool and copy it to the
mindspore/lite/examples/cloud_infer/quick_start_parallel_pythondirectory. You can download the MobileNetV2 model file mobilenetv2.mindir and input data input.bin.Install the MindSpore Lite cloud-side inference Python package for Python version 3.7 via pip.
python -m pip install https://ms-release.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com/${MINDSPORE_LITE_VERSION}/MindSpore/lite/release/centos_x86/cloud_fusion/mindspore_lite-${MINDSPORE_LITE_VERSION}-cp37-cp37m-linux_x86.whl --trusted-host ms-release.obs.cn-north-4.myhuaweicloud.com -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
Creating configuration context
The Context.parallel attributes, context related to multi-model concurrent inference, will hold some basic configuration parameters required for concurrent inference to guide the number of concurrent models as well as model compilation and model execution.
The following sample code demonstrates how to set Context.parallel attributes and configure the number of workers for concurrent inference.
import time
from threading import Thread
import numpy as np
import mindspore_lite as mslite
# the number of threads of one worker.
# WORKERS_NUM * THREAD_NUM should not exceed the number of cores of the machine.
THREAD_NUM = 1
# In parallel inference, the number of workers in one `ModelParallelRunner` in server.
# If you prepare to compare the time difference between parallel inference and serial inference,
# you can set WORKERS_NUM = 1 as serial inference.
WORKERS_NUM = 3
# Simulate 5 clients, and each client sends 2 inference tasks to the server at the same time.
PARALLEL_NUM = 5
TASK_NUM = 2
THREAD_NUM: The number of threads in a single worker.WORKERS_NUM * THREAD_NUMshould be less than the number of machine cores.WORKERS_NUM: On the server side, specify the number of workers in aModelParallelRunner, i.e., the units that perform concurrent inference. If you want to compare the difference in inference time between concurrent inference and non-concurrent inference, you can setWORKERS_NUMto 1 for comparison.PARALLEL_NUM: The number of concurrent, i.e., the number of clients that are sending inference task requests at the same time.TASK_NUM: The number of tasks, i.e., the number of inference task requests sent by a single client.
# Init RunnerConfig and context, and add CPU device info
context = mslite.Context()
context.target = ["cpu"]
context.cpu.thread_num = THREAD_NUM
context.cpu.inter_op_parallel_num = THREAD_NUM
context.parallel.workers_num = WORKERS_NUM
The configuration method of the Context is detailed in Context.
Multi-model concurrent inference does not support FP32 type data inference. CPU pinning only supports unbinding or binding large cores, does not support the parameter setting of binding middle cores, and does not support the configuration of binding core list.
ModelParallelRunner creation and compilation
When using MindSpore Lite to perform concurrent inference, ModelParallelRunner is the main entry point for concurrent inference, you need to call build_from_file interface of ModelParallelRunner for ModelParallelRunner loading and compilation.
# Build ModelParallelRunner from file
model_parallel_runner = mslite.ModelParallelRunner()
model_parallel_runner.build_from_file(model_path="./model/mobilenetv2.mindir", context=context)
If it is not configured, it will be set cpu target, and automatically set cpu attributes by default.
Setting Concurrent Inference Tasks
Create multiple threads and bind concurrent inference tasks. The inference tasks include padding data into input Tensor, using predict interface of ModelParallelRunner for concurrent inference and getting inference results via the output Tensor.
def parallel_runner_predict(parallel_runner, parallel_id):
"""
One Runner with 3 workers, set model input, execute inference and get output.
Args:
parallel_runner (mindspore_lite.ModelParallelRunner): Actuator Supporting Parallel inference.
parallel_id (int): Simulate which client's task to process
"""
task_index = 0
while True:
if task_index == TASK_NUM:
break
task_index += 1
# Set model input
inputs = parallel_runner.get_inputs()
in_data = np.fromfile("./model/input.bin", dtype=np.float32)
inputs[0].set_data_from_numpy(in_data)
once_start_time = time.time()
# Execute inference
outputs = parallel_runner.predict(inputs)
once_end_time = time.time()
print("parallel id: ", parallel_id, " | task index: ", task_index, " | run once time: ",
once_end_time - once_start_time, " s")
# Get output
for output in outputs:
tensor_name = output.name.rstrip()
data_size = output.data_size
element_num = output.element_num
print("tensor name is:%s tensor size is:%s tensor elements num is:%s" % (tensor_name,
data_size,
element_num))
data = output.get_data_to_numpy()
data = data.flatten()
print("output data is:", end=" ")
for j in range(5):
print(data[j], end=" ")
print("")
# The server creates 5 threads to store the inference tasks of 5 clients.
threads = []
total_start_time = time.time()
for i in range(PARALLEL_NUM):
threads.append(Thread(target=parallel_runner_predict, args=(model_parallel_runner, i,)))
Performing Concurrent Inference
Start a multi-thread and execute the configured concurrent inference task. During the execution, the single inference time and inference result in concurrent inference are printed, and the total concurrent inference time is printed after the end of the thread.
# Start threads to perform parallel inference.
for th in threads:
th.start()
for th in threads:
th.join()
total_end_time = time.time()
print("total run time: ", total_end_time - total_start_time, " s")