Experiencing C-language Simplified Inference Demo
Overview
This tutorial provides a sample program for MindSpore Lite to perform inference, which demonstrates the basic process of end-side inference with C-language by randomly typing, performing inference, and printing inference results, so that users can quickly understand the use of MindSpore Lite to perform inference-related APIs. This tutorial performs the inference of MobileNetV2 model by taking randomly generated data as input data and prints obtained output data. The related code is in the mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_c directory.
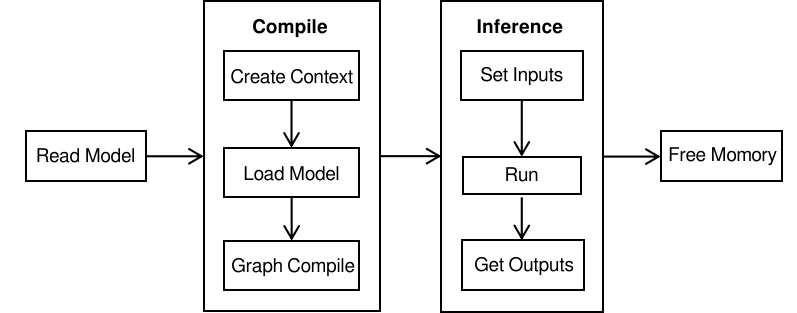
Performing inference with MindSpore Lite consists of the following main steps:
Read model: Read the
.msmodel converted by Model Conversion Tool from the file system.Create configuration context: Create a Configuration Context that holds some basic configuration parameters needed, to guide model compilation and model execution.
Create, load and compile Model: Before executing inference, you need to call MSModelBuildFromFile interface of Model for model loading and compilation, and configure the Context obtained in the previous step into the Model. The model loading phase parses the file cache into a runtime model. The model compilation phase mainly carries out the process of operator selection scheduling, subgraph slicing, etc, which will consume more time, so it is recommended that the Model be created once, compiled once, and reasoned several times.
Input data: The data needs to be padded in the
Input Tensorbefore model execution.Execute inference: Use MSModelPredict inferene of Model for model inference.
Obtain output: After the model execution, the inference result can be obtained by
output Tensor.Free memory: When do not need to use MindSpore Lite inference framework, you need to free the created Model.
Building and Running the Demo
Linux X86
Environment requirements
Compiling and building
Execute the build script in
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_cdirectory, which will automatically download the MindSpore Lite inference framework library and the model file and compile the Demo.bash build.shIf the build script fails to download the MindSpore Lite inference framework, please manually download the MindSpore Lite model inference framework mindspore-lite-{version}-linux-x64.tar.gz for the CPU hardware platform and Ubuntu-x64 operating system, after decompression copy the
libmindspore-lite.sofile from the unpackedruntime/libdirectory tomindspore/ lite/examples/quick_start_c/libdirectory, and the files inruntime/includedirectory tomindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_c/includedirectory, and copy thelibmindspore_glog.so.0file from theruntime/third_party/glogdirectory to thelibmindspore_glog.sofile inmindspore/ lite/examples/quick_start_c/libdirectory.If the build script fails to download the MobileNetV2 model, please manually download the relevant model file mobilenetv2.ms and copy it to the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_c/modeldirectory.After manually downloading and placing the files in the specified location, the build.sh script needs to be executed again to complete the compiling and building.
Executing inference
After compiling and building, go to the
mindspore/lite/examples/quick_start_c/builddirectory and execute the following command to experience the MobileNetV2 model inference by MindSpore Lite../mindspore_quick_start_c ../model/mobilenetv2.msWhen the execution is completed, the following results will be obtained. Print the name, the size and the number of the output Tensor and the first 50 data:
Tensor name: Softmax-65, tensor size is 4004 ,elements num: 1001. output data is: 0.000011 0.000015 0.000015 0.000079 0.000070 0.000702 0.000120 0.000590 0.000009 0.000004 0.000004 0.000002 0.000002 0.000002 0.000010 0.000055 0.000006 0.000010 0.000003 0.000010 0.000002 0.000005 0.000001 0.000002 0.000004 0.000006 0.000008 0.000003 0.000015 0.000005 0.000011 0.000020 0.000006 0.000002 0.000011 0.000170 0.000005 0.000009 0.000006 0.000002 0.000003 0.000009 0.000005 0.000006 0.000003 0.000011 0.000005 0.000027 0.000003 0.000050 0.000016
Windows
Environment requirements
Compiling and building
Library downloading: Please manually download the MindSpore Lite model inference framework mindspore-lite-{version}-win-x64.zip with CPU as the hardware platform and Windows-x64 as the operating system, after decompression copy all files in the
runtime\libdirectory to themindspore\lite\examples\quick_start_clib\project directory, and the files in theruntime\includedirectory to themindspore\lite\examples\quick_start_c\includeproject directory. (Note: thelibandincludedirectories under the project need to be created manually)Model downloading: Please manually download the relevant model file mobilenetv2.ms and copy it to the
mindspore\ lite\examples\quick_start_c\modeldirectory.Compiling: Execute the build script in the
mindspore\lite\examples\quick_start_cdirectory, which can automatically download the relevant files and compile the Demo.
call build.batExecuting inference
After compiling and building, go to the
mindspore\lite\examples\quick_start_c\builddirectory and execute the following command to experience the MobileNetV2 model inference by MindSpore Lite.set PATH=..\lib;%PATH% call mindspore_quick_start_c.exe ..\model\mobilenetv2.ms
When the execution is completed, the following results will be obtained. Print the name, the size and the number of the output Tensor and the first 50 data:
Tensor name: Softmax-65, tensor size is 4004 ,elements num: 1001. output data is: 0.000011 0.000015 0.000015 0.000079 0.000070 0.000702 0.000120 0.000590 0.000009 0.000004 0.000004 0.000002 0.000002 0.000002 0.000010 0.000055 0.000006 0.000010 0.000003 0.000010 0.000002 0.000005 0.000001 0.000002 0.000004 0.000006 0.000008 0.000003 0.000015 0.000005 0.000011 0.000020 0.000006 0.000002 0.000011 0.000170 0.000005 0.000009 0.000006 0.000002 0.000003 0.000009 0.000005 0.000006 0.000003 0.000011 0.000005 0.000027 0.000003 0.000050 0.000016
Configuring CMake
The following is sample code when the libmindspore-lite.so static library is integrated via CMake.
The
-wl,--whole-archiveoption needs to be passed to the linker when thelibmindspore-lite.sostatic library is integrated.Since the
-fstack-protector-strongstack-protected compiling option was added when compiling MindSpore Lite, it is also necessary to link thessplibrary in MinGW on the Windows platform.Since support for so library file handling was added when compiling MindSpore Lite, it is also necessary to link the
dllibrary on the Linux platform.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.18.3)
project(QuickStartC)
if(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID STREQUAL "GNU" AND CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION VERSION_LESS 7.3.0)
message(FATAL_ERROR "GCC version ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_VERSION} must not be less than 7.3.0")
endif()
# Add directory to include search path
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR})
# Add directory to linker search path
link_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
file(GLOB_RECURSE QUICK_START_CXX ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/*.cc)
add_executable(mindspore_quick_start_c ${QUICK_START_CXX})
target_link_libraries(
mindspore_quick_start_c
-Wl,--whole-archive libmindspore-lite -Wl,--no-whole-archive
pthread
)
# Due to the increased compilation options for stack protection,
# it is necessary to target link ssp library when Use the static library in Windows.
if(WIN32)
target_link_libraries(
mindspore_quick_start_c
ssp
)
else()
target_link_libraries(
mindspore_quick_start_c
dl
)
endif()
Creating Configuration Context
// Create and init context, add CPU device info
MSContextHandle context = MSContextCreate();
if (context == NULL) {
printf("MSContextCreate failed.\n");
return kMSStatusLiteError;
}
const int thread_num = 2;
MSContextSetThreadNum(context, thread_num);
MSContextSetThreadAffinityMode(context, 1);
MSDeviceInfoHandle cpu_device_info = MSDeviceInfoCreate(kMSDeviceTypeCPU);
if (cpu_device_info == NULL) {
printf("MSDeviceInfoCreate failed.\n");
MSContextDestroy(&context);
return kMSStatusLiteError;
}
MSDeviceInfoSetEnableFP16(cpu_device_info, false);
MSContextAddDeviceInfo(context, cpu_device_info);
Creating, Loading and Compiling Model
Model loading and compilation can be done by calling MSModelBuildFromFile interface of Model to load and compile from the file path to get the runtime model. In this case, argv[1] corresponds to the model file path inputted from the console.
// Create model
MSModelHandle model = MSModelCreate();
if (model == NULL) {
printf("MSModelCreate failed.\n");
MSContextDestroy(&context);
return kMSStatusLiteError;
}
// Build model
int ret = MSModelBuildFromFile(model, argv[1], kMSModelTypeMindIR, context);
if (ret != kMSStatusSuccess) {
printf("MSModelBuildFromFile failed, ret: %d.\n", ret);
MSModelDestroy(&model);
return ret;
}
Model Inference
The model inference mainly includes the steps of input data, inference execution, and obtaining output, where the input data in this example is generated by random data, and finally the output result after execution of inference is printed.
// Get Inputs
MSTensorHandleArray inputs = MSModelGetInputs(model);
if (inputs.handle_list == NULL) {
printf("MSModelGetInputs failed, ret: %d.\n", ret);
MSModelDestroy(&model);
return ret;
}
// Generate random data as input data.
ret = GenerateInputDataWithRandom(inputs);
if (ret != kMSStatusSuccess) {
printf("GenerateInputDataWithRandom failed, ret: %d.\n", ret);
MSModelDestroy(&model);
return ret;
}
// Model Predict
MSTensorHandleArray outputs;
ret = MSModelPredict(model, inputs, &outputs, NULL, NULL);
if (ret != kMSStatusSuccess) {
printf("MSModelPredict failed, ret: %d.\n", ret);
MSModelDestroy(&model);
return ret;
}
// Print Output Tensor Data.
for (size_t i = 0; i < outputs.handle_num; ++i) {
MSTensorHandle tensor = outputs.handle_list[i];
int64_t element_num = MSTensorGetElementNum(tensor);
printf("Tensor name: %s, tensor size is %ld ,elements num: %ld.\n", MSTensorGetName(tensor),
MSTensorGetDataSize(tensor), element_num);
const float *data = (const float *)MSTensorGetData(tensor);
printf("output data is:\n");
const int max_print_num = 50;
for (int j = 0; j < element_num && j <= max_print_num; ++j) {
printf("%f ", data[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
Freeing memory
When do not need to use MindSpore Lite inference framework, you need to free the Model that has been created.
// Delete model.
MSModelDestroy(&model);