应用SLB算法
背景
传统的量化方法在计算梯度时,通常使用STE(Straight Through Estimator) [1]或者自行设计的梯度计算方式[2]。量化函数的不可微往往会导致计算出来的梯度有误差,从而提供不准确的优化方向,导致最终推理精度比较差。因此,迫切需要一种能规避这种不准确梯度估计的量化神经网络学习方法。
算法原理介绍
SLB(Searching for low-bit weights) [3]是华为诺亚自研的权重量化算法,提供了一种基于权值搜索的低比特量化算法,能避开不准确的梯度估计。针对低比特网络量化,由于量化网络权值的有效解数量比较少,因此,对网络的量化可以通过对权值搜索实现,即将量化过程转换成权值搜索的过程。对给定量化网络预设一组量化权值,然后定义一个概率矩阵来表示不同量化权值被保留的概率,在训练阶段通过优化概率矩阵实现网络权重的量化。
下面左边图是用传统量化算法做二值量化,训练时用不准确的梯度更新浮点权重,最后对浮点权重做二值化(用sigmoid函数)处理得到量化权重。右边图是用SLB量化算法做二值量化,利用连续松弛策略搜索离散权重,训练时优化离散权重的权值概率矩阵,最后根据概率挑选离散权重实现量化。左边图中红色点对应的单个值是由sigmoid函数得到,表示权重被量化为-1的概率。蓝色点对应的单个值是由sigmoid函数得到,表示权重被量化为+1的概率。传统量化算法中不准确的梯度更新会影响浮点权重的更新,从而导致这里的概率出现较大的偏差。右边图中红蓝相间的点对应的2个值是由softmax函数得到,表示权重被量化为-1或+1的概率。由于避开了不准确的梯度更新,这里的概率会更精准。
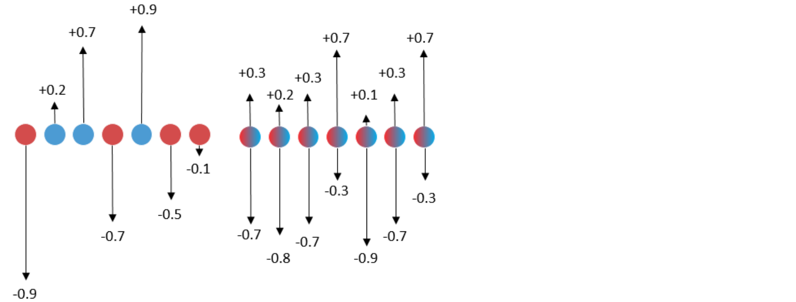
温度因子
在分类任务中,softmax分布通常用于计算输出被分为各个类的概率。因此,SLB也使用softmax分布来计算权重被量化为各个量化权值的概率,并最终根据最大概率挑选对应权值作为量化结果。为了提高量化结果的置信度,SLB引入了温度因子,通过逐步调整温度因子,能使softmax分布逐渐变得陡峭,慢慢趋近于one-hot分布,从而最大化量化结果的置信度,缩减量化误差。
下面左边公式是标准的softmax函数,右边是SLB算法中引入了温度因子后的softmax函数。
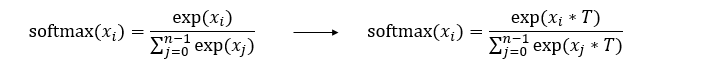
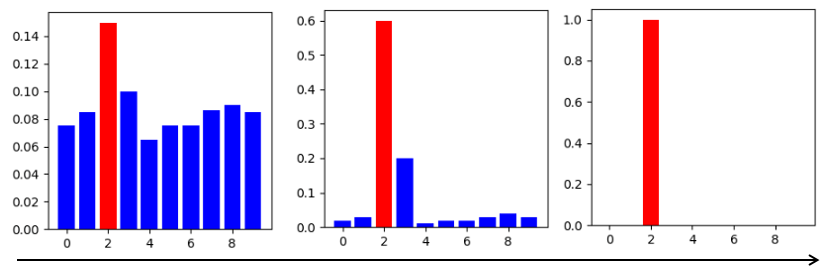
下图展示了逐步调整温度因子时,softmax分布的变化过程,最右侧是one-hot分布。
算法特点
提出了一种新的权值搜索方法,用于训练量化深度神经网络,能规避不准确梯度估计。
利用连续松弛策略搜索离散权重,训练时优化离散权重的概率分布,最后根据概率挑选离散权重实现量化。
为了进一步消除搜索后的推理精度差距,保证训练和测试的一致性,提出了逐步调整温度因子的策略。
与传统的量化算法相比,规避了不准确的梯度更新过程,能获得更高的推理精度,在极低比特量化中更有优势。
SLB量化训练
SLB量化算法的训练规格如下表所示。
表1:SLB量化训练规格
规格 |
规格说明 |
|---|---|
硬件支持 |
GPU |
网络支持 |
ResNet18,具体请参见https://gitee.com/mindspore/models/tree/r2.0/official/cv/ResNet#应用mindspore-golden-stick模型压缩算法。 |
方案支持 |
支持1、2、4比特的权重量化方案,支持8比特的激活量化方案。 |
数据类型支持 |
GPU平台支持FP32。 |
运行模式支持 |
Graph模式和PyNative模式。 |
SLB量化训练示例
SLB量化训练与一般训练步骤一致,在定义量化网络和生成量化模型阶段需要进行额外的操作,完整流程如下:
加载数据集,处理数据。
定义网络。
定义SLB量化算法,应用算法生成量化模型。
定义优化器、损失函数和callbacks。
训练网络,保存模型文件。
加载模型文件,对比量化后精度。
接下来以ResNet18网络为例,分别叙述这些步骤。
加载数据集
dataset = create_dataset(dataset_path=config.data_path, do_train=True,
batch_size=config.batch_size, train_image_size=config.train_image_size,
eval_image_size=config.eval_image_size, target=config.device_target,
distribute=config.run_distribute)
代码中create_dataset引用自dataset.py,config.data_path和config.batch_size分别在配置文件中配置,下同。
定义原网络
from src.resnet import resnet18 as resnet
...
net = resnet(class_num=config.class_num)
print(net)
原始网络结构如下:
ResNet<
(conv1): Conv2d<input_channels=3, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), pad_mode=pad, padding=3, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn1): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, gamma=Parameter (name=bn1.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=bn1.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=bn1.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=bn1.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(pad): Pad<>
(maxpool): MaxPool2d<kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode=VALID>
(layer1): SequentialCell<
(0): ResidualBlockBase<
(conv1): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn1d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn1d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn1d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn1d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn1d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(conv2): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn2d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn2d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn2d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn2d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1.0.bn2d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(relu): ReLU<>
>
(1): ResidualBlockBase<
(conv1): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn1d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn1d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn1d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn1d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn1d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(conv2): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn2d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn2d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn2d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn2d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1.1.bn2d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(relu): ReLU<>
>
>
(layer2): SequentialCell<...>
(layer3): SequentialCell<...>
(layer4): SequentialCell<...>
(flatten): Flatten<>
(end_point): Dense<input_channels=512, output_channels=10, has_bias=True>
>
ResNet18网络定义见resnet.py。
应用量化算法
量化网络是指在原网络定义的基础上,修改需要量化的网络层后生成的带有伪量化节点的网络,通过构造MindSpore Golden Stick下的SlbQuantAwareTraining类,并将其应用到原网络上将原网络转换为量化网络。
from mindspore_gs import SlbQuantAwareTraining as SlbQAT
from mindspore import QuantDtype
...
algo = SlbQAT()
algo.set_weight_quant_dtype(QuantDtype.INT1)
algo.set_act_quant_dtype(QuantDtype.INT8)
algo.set_enable_act_quant(True)
algo.set_enable_bn_calibration(True)
algo.set_epoch_size(100)
algo.set_has_trained_epoch(0)
algo.set_t_start_val(1.0)
algo.set_t_start_time(0.2)
algo.set_t_end_time(0.6)
algo.set_t_factor(1.2)
quant_net = algo.apply(net)
print(algo)
print(quant_net)
打印量化器,会得到如下的信息,其中包含各个属性的配置信息,可以用来检查算法是否配置成功。
SlbQuantAwareTraining<weight_quant_dtype=INT1, act_quant_dtype=INT8, enable_act_quant=True, enable_bn_calibration=True, epoch_size=100, has_trained_epoch=0, t_start_val=1.0, t_start_time=0.2, t_end_time=0.6, t_factor=1.2>
打印量化后的网络,会得到如下的网络结构,其中QuantizeWrapperCell为SLB量化对原有Conv2d的封装类,包括了原有的算子和权重的伪量化节点,用户可以参考API 修改算法配置,并通过检查QuantizeWrapperCell的属性确认算法是否配置成功。
ResNetOpt<
(_handler): ResNet<...>
(conv1): Conv2d<input_channels=3, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(7, 7), stride=(2, 2), pad_mode=pad, padding=3, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn1): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.9, gamma=Parameter (name=bn1.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=bn1.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=bn1.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=bn1.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(pad): Pad<>
(maxpool): MaxPool2d<kernel_size=3, stride=2, pad_mode=VALID>
(layer1): SequentialCellOpt<
(_handler): SequentialCell<...>
(cell_list_0): ResidualBlockBaseOpt<
(_handler): ResidualBlockBase<...>
(conv1): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn1d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn1d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn1d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn1d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn1d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(conv2): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn2d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn2d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn2d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn2d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.0.bn2d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(relu): ReLU<>
(Conv2dSlbQuant): QuantizeWrapperCell<
(_handler): Conv2dSlbQuant<
in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), weight_bit_num=1, stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False
(fake_quant_weight): SlbFakeQuantizerPerLayer<bit_num=1>
>
(_input_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
(_output_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
>
(Conv2dSlbQuant_1): QuantizeWrapperCell<
(_handler): Conv2dSlbQuant<
in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), weight_bit_num=1, stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False
(fake_quant_weight): SlbFakeQuantizerPerLayer<bit_num=1>
>
(_input_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
(_output_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
>
>
(cell_list_1): ResidualBlockBaseOpt_1<
(_handler): ResidualBlockBase<...>
(conv1): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn1d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn1d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn1d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn1d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn1d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(conv2): Conv2d<input_channels=64, output_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False, weight_init=..., bias_init=zeros, format=NCHW>
(bn2d): BatchNorm2d<num_features=64, eps=0.0001, momentum=0.09999999999999998, gamma=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn2d.gamma, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), beta=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn2d.beta, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=True), moving_mean=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn2d.moving_mean, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False), moving_variance=Parameter (name=layer1._handler.1.bn2d.moving_variance, shape=(64,), dtype=Float32, requires_grad=False)>
(relu): ReLU<>
(Conv2dSlbQuant): QuantizeWrapperCell<
(_handler): Conv2dSlbQuant<
in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), weight_bit_num=1, stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False
(fake_quant_weight): SlbFakeQuantizerPerLayer<bit_num=1>
>
(_input_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
(_output_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
>
(Conv2dSlbQuant_1): QuantizeWrapperCell<
(_handler): Conv2dSlbQuant<
in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(3, 3), weight_bit_num=1, stride=(1, 1), pad_mode=pad, padding=1, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False
(fake_quant_weight): SlbFakeQuantizerPerLayer<bit_num=1>
>
(_input_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
(_output_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
>
>
>
(layer2): SequentialCellOpt_1<...>
(layer3): SequentialCellOpt_3<...>
(layer4): SequentialCellOpt_5<...>
(flatten): Flatten<>
(end_point): Dense<input_channels=512, output_channels=10, has_bias=True>
(Conv2dSlbQuant): QuantizeWrapperCell<
(_handler): Conv2dSlbQuant<
in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=(7, 7), weight_bit_num=1, stride=(2, 2), pad_mode=pad, padding=3, dilation=(1, 1), group=1, has_bias=False
(fake_quant_weight): SlbFakeQuantizerPerLayer<bit_num=1>
>
(_input_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
(_output_quantizer): SlbActQuantizer<bit_num=8, symmetric=False, narrow_range=False, ema=False(0.999), per_channel=False, quant_delay=900>
>
>
与原网络相比,量化后的网络里面的conv被替换成了Conv2dSlbQuant。
定义优化器、损失函数和训练的callbacks
对于SLB量化算法,除了要定义训练中常用的callbacks,还需要通过调用SlbQuantAwareTraining类的callbacks接口来定义SLB量化算法特有的一些callbacks,其中包括用于调节温度因子的callback。
import mindspore as ms
import mindspore.train.callback as callback
from mindspore.amp import FixedLossScaleManager
from mindspore.train import ModelCheckpoint, CheckpointConfig, LossMonitor, TimeMonitor, Model
step_size = dataset.get_dataset_size()
lr = get_lr(lr_init=config.lr_init,
lr_end=config.lr_end,
lr_max=config.lr_max,
warmup_epochs=config.warmup_epochs,
total_epochs=config.epoch_size,
steps_per_epoch=step_size,
lr_decay_mode=config.lr_decay_mode)
if config.pre_trained:
lr = lr[config.has_trained_epoch * step_size:]
lr = ms.Tensor(lr)
# define optimizer
group_params = init_group_params(quant_net)
opt = nn.Momentum(group_params, lr, config.momentum, weight_decay=config.weight_decay,
loss_scale=config.loss_scale)
loss = init_loss_scale()
loss_scale = FixedLossScaleManager(config.loss_scale, drop_overflow_update=False)
metrics = {"acc"}
model = Model(quant_net, loss_fn=loss, optimizer=opt, loss_scale_manager=loss_scale, metrics=metrics,
amp_level="O0", boost_level=config.boost_mode, keep_batchnorm_fp32=False,
eval_network=None,
boost_config_dict={"grad_freeze": {"total_steps": config.epoch_size * step_size}})
# define callbacks
time_cb = TimeMonitor(data_size=step_size)
loss_cb = LossCallBack(config.has_trained_epoch)
cb = [time_cb, loss_cb]
algo_cb_list = algo.callbacks(model, dataset)
cb += algo_cb_list
ckpt_append_info = [{"epoch_num": config.has_trained_epoch, "step_num": config.has_trained_step}]
config_ck = CheckpointConfig(save_checkpoint_steps=config.save_checkpoint_epochs * step_size,
keep_checkpoint_max=config.keep_checkpoint_max,
append_info=ckpt_append_info)
ckpt_cb = ModelCheckpoint(prefix="resnet", directory="./ckpt", config=config_ck)
cb += [ckpt_cb]
代码中get_lr引用自lr_generator.py,init_group_params和init_loss_scale都引用自train.py。
训练模型,保存模型文件
定义好模型后,开始进行训练。
dataset_sink_mode = target != "CPU"
model.train(config.epoch_size - config.has_trained_epoch, dataset, callbacks=cb,
sink_size=dataset.get_dataset_size(), dataset_sink_mode=dataset_sink_mode)
运行部分结果如下:
epoch: 1 step: 1562, loss is 1.4536957
Train epoch time: 101539.306 ms, per step time: 65.006 ms
epoch: 2 step: 1562, loss is 1.3616204
Train epoch time: 94238.882 ms, per step time: 60.332 ms
epoch: 3 step: 1562, loss is 1.2128768
Train epoch time: 94237.197 ms, per step time: 60.331 ms
epoch: 4 step: 1562, loss is 0.99068344
Train epoch time: 94084.353 ms, per step time: 60.233 ms
epoch: 5 step: 1562, loss is 0.89842224
Train epoch time: 94498.564 ms, per step time: 60.498 ms
epoch: 6 step: 1562, loss is 0.8985137
Train epoch time: 94106.722 ms, per step time: 60.248 ms
加载模型,对比精度
按照resnet模型仓步骤获得普通训练的模型精度:
'top_1_accuracy': 0.9544270833333334, 'top_5_accuracy': 0.9969951923076923
加载上一步得到的模型文件,导入量化后模型评估精度。
param_dict = ms.load_checkpoint(config.checkpoint_file_path)
ms.load_param_into_net(quant_net, param_dict)
ds_eval = create_dataset(dataset_path=config.data_path, do_train=False, batch_size=config.batch_size,
eval_image_size=config.eval_image_size, target=config.device_target)
model = Model(quant_net, loss_fn=loss, metrics={'top_1_accuracy', 'top_5_accuracy'})
acc = model.eval(ds_eval)
print(acc)
'top_1_accuracy': 0.9466145833333334, 'top_5_accuracy': 0.9964050320512820.
算法效果汇总
-表示尚未测试,NS表示尚未支持
训练效果
使用图模式进行训练,使用的代码为:MindSpore,MindSpore Golden Stick,MindSpore Models。
W4表示weight权重量化为4bit,W2表示权重量化为2bit,W1表示权重量化为1bit,A8表示激活量化为8bit。
算法 |
网络 |
数据集 |
CUDA11 Top1Acc |
CUDA11 Top5Acc |
Ascend910 Top1Acc |
Ascend910 Top5Acc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
baseline |
resnet18 |
CIFAR10 |
94.25% |
99.93% |
- |
- |
SLB W4 |
resnet18 |
CIFAR10 |
95.18% |
99.67% |
NS |
NS |
SLB W2 |
resnet18 |
CIFAR10 |
95.12% |
99.68% |
NS |
NS |
SLB W1 |
resnet18 |
CIFAR10 |
95.23% |
99.87% |
NS |
NS |
baseline |
resnet18 |
Imagenet2012 |
70.14% |
89.71% |
- |
- |
SLB W4 |
resnet18 |
Imagenet2012 |
68.65% |
88.57% |
NS |
NS |
SLB W2 |
resnet18 |
Imagenet2012 |
68.42% |
88.40% |
NS |
NS |
SLB W1 |
resnet18 |
Imagenet2012 |
66.75% |
87.08% |
NS |
NS |
可以发现,与全精度模型相比,4bit权重量化后的模型top1精度没有损失,1bit权重量化的top1精度损失在0.6%以内。在做了权重量化后,再做8bit激活量化,top1精度损失在0.4%以内。SLB量化大幅降低了模型的参数量和计算量,使得在资源受限的环境部署AI能力变得更加便利。需要注意的是,此处量化网络并非最终部署网络,由于增加了伪量化节点和权值概率矩阵,ckpt大小相较原始网络有较大程度的增加,增幅受权重量化比特影响,量化的比特数越大增幅越大。
参考文献
[1] Bengio, Yoshua, Nicholas Léonard, and Aaron Courville. Estimating or propagating gradients through stochastic neurons for conditional computation. 2013.
[2] Hanxiao Liu, Karen Simonyan, and Yiming Yang. Darts: Differentiable architecture search. ICLR, 2019.
[3] Yang Z, Wang Y, Han K, et al. Searching for low-bit weights in quantized neural networks. NIPS, 2020.
